Recombinant Human Protein Mdm4 (MDM4)
-
中文名稱:人MDM4重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-YP013627HU
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:人MDM4重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP013627HU-B
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:人MDM4重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-BP013627HU
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:人MDM4重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-MP013627HU
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:DKFZp781B1423; Double minute 4; Double minute 4 human homolog of p53 binding protein; Double minute 4 protein; HDMX; MDM 4; Mdm2 like p53 binding protein; Mdm2-like p53-binding protein; MDM4; Mdm4 p53 binding protein homolog mouse; Mdm4 protein; MDM4 related protein 1; Mdm4 transformed 3T3 cell double minute 4; Mdm4 transformed 3T3 cell double minute 4 p53 binding protein; Mdm4 transformed 3T3 cell double minute 4 p53 binding protein mouse; MDM4_HUMAN; Mdmx protein; MGC132766; Mouse double minute 4 homolog; Mouse double minute 4 human homolog of p53 binding protein; MRP 1; MRP1; p53 binding protein; p53 BINDING PROTEIN MDM4; p53-binding protein Mdm4; Protein Mdm4; Protein Mdmx
-
種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白長度:Full length protein
-
表達區(qū)域:1-490
-
氨基酸序列MTSFSTSAQC STSDSACRIS PGQINQVRPK LPLLKILHAA GAQGEMFTVK EVMHYLGQYI MVKQLYDQQE QHMVYCGGDL LGELLGRQSF SVKDPSPLYD MLRKNLVTLA TATTDAAQTL ALAQDHSMDI PSQDQLKQSA EESSTSRKRT TEDDIPTLPT SEHKCIHSRE DEDLIENLAQ DETSRLDLGF EEWDVAGLPW WFLGNLRSNY TPRSNGSTDL QTNQDVGTAI VSDTTDDLWF LNESVSEQLG VGIKVEAADT EQTSEEVGKV SDKKVIEVGK NDDLEDSKSL SDDTDVEVTS EDEWQCTECK KFNSPSKRYC FRCWALRKDW YSDCSKLTHS LSTSDITAIP EKENEGNDVP DCRRTISAPV VRPKDAYIKK ENSKLFDPCN SVEFLDLAHS SESQETISSM GEQLDNLSEQ RTDTENMEDC QNLLKPCSLC EKRPRDGNII HGRTGHLVTC FHCARRLKKA GASCPICKKE IQLVIKVFIA
-
蛋白標簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相關產(chǎn)品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Along with MDM2, contributes to TP53 regulation. Inhibits p53/TP53- and TP73/p73-mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by binding its transcriptional activation domain. Inhibits degradation of MDM2. Can reverse MDM2-targeted degradation of TP53 while maintaining suppression of TP53 transactivation and apoptotic functions.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- Considering the lack of association between MDM4 rs4245739 polymorphism and breast cancer, rs4245739 polymorphism of this gene seems to have no significant role in the pathophysiology of the disease. PMID: 28164646
- We conclude that Mdm4-S overexpression is a consequence of splicing defects in tumor cells rather than a cause of tumor evolution. PMID: 28460439
- These results indicate that the rs4245739 polymorphism may contribute to a decreased cancer susceptibility and support the hypothesis that genetic variants in the MDM4 genes act as important modifiers of cancer risk. PMID: 27738340
- our study is the first to identify miR-766 as a novel p53 activator that functions by targeting MDM4 and thereby enhancing the p53 signalling axis. PMID: 28430625
- High MDM4 expression levels are associated with lymph node metastasis of gastric adenocarcinoma and influence the prognosis of patients with gastric adenocarcinoma PMID: 27626496
- MDM4 rs4245739 A > C polymorphism appears to be associated with decreased cancer risk PMID: 27687591
- analyses indicated that rs4245739 polymorphism in the MDM4 gene may play an important role in the etiology of cancer PMID: 27742919
- results revealed an allosteric ligand-binding mechanism of the N-terminal domain of MdmX in which the ligand initially interacts with a compact core, followed by augmenting intermolecular interactions with intrinsic flexible regions PMID: 29023092
- Complex alterations of HDM4 proteins, which are critical regulators of cell cycle progression, are frequent defects in AML and HG-MDS cases. The overall rates of detection of HDM4 expression in the present study, 92% in AML and 52% in MDS, respectively, indicate that HDM4 is a potential therapeutic target in patients with these diseases. PMID: 27155969
- MDM4 rs1380576 G variant is associated with gastric cancer. PMID: 28099948
- These results demonstrate that cisplatin-mediated p53(V172F) mutation regulates p53 stability at the normothermic temperature, but it is the increased recruitment of MDM4 by the homomeric or heteromeric mutant p53(V172F) complex that inhibits p53-dependent transactivation. This represents a novel cellular mechanism of p53 inhibition, and, thereby, induction of cisplatin resistance PMID: 26876197
- MDM4 protein is frequently abundant in the context of mutant p53 in basal-like breast cancer (BC) samples. MDM4 plays a critical role in the proliferation of these BC cells. MDM4 is crucial for the establishment and progression of tumours. PMID: 28097652
- Study used polymer statistics to estimate a global KD value for p53 binding to MdmX in the presence of the flexible linker and the intramolecular binding motif by assuming the flexible linker behaves as a wormlike chain. Calculations and measurements showed that the intramolecular binding motif reduces the apparent affinity of p53 for MdmX by a factor of 400. PMID: 28487147
- Data indicate that knockdown of otubain 1 protein (Otub1) reduced the levels of double minute 4 protein (MDMX). PMID: 28035068
- these data identify MDM4 as a nutrient-sensor able to inhibit mTORC1 and highlight its metabolism-related tumor-suppressing function. PMID: 28270148
- Data indicate that two single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs)rs10900598 and rs4245739, located at 3'-untranslated region (UTR) of double minute 4 protein (MDM4) gene, contribute to clinical outcome of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients treated with platinum-based chemotherapy. PMID: 27462918
- identified a novel Her4-induced posttranslational modification on MDMX PMID: 27777309
- MDM4 SNP34091 polymorphism may function as a protective factor against cancer risk. PMID: 27646776
- Individuals harboring the MDM4 SNP34091AC/CC genotypes had a significantly elevated risk for serous ovarian cancer, particularly high-grade serous ovarian cancer. No association between SNP34091 genotypes and endometrial cancer risk was observed. PMID: 26867771
- These results suggest that secondary intermolecular interaction is important in p53 regulation by MDMX, which may represent a common phenomenon in complexes containing multidomain proteins. PMID: 27114532
- Authors show that the EMT phenotype in multiple cellular models and in clinical prostate and breast cancer samples is associated with a decrease in MDM2 and increase in MDMX expression. PMID: 26416355
- MDM4 SNP34091 status to be associated with reduced risk of breast cancer, in particular in individuals carrying the MDM2 SNP309GG genotype, but not to be associated with either lung-, colon- or prostate cancer. PMID: 26471763
- The phosphate group of pTyr99 imposes extensive steric clashes with the C-terminus of p53 peptide and induces a significant lateral shift of the peptide ligand, decreasing the binding affinity of MDMX for p53. PMID: 26148237
- MDM4/HIPK2/p53 cytoplasmic assembly uncovers coordinated repression of molecules with anti-apoptotic activity during early DNA damage response. PMID: 25961923
- MDM4 rs4245739 single nucleotide polymorphism contributes to small cell lung cancer risk and support the notion that gene 3'-UTR genetic variants, impacting miRNA-binding, might modify small cell lung cancer susceptibility. PMID: 26274820
- These results identify Mdmx growth dependency in wt p53 expressing breast cancer across a range of subtypes. Based on our findings, we propose that Mdmx targeting is an attractive strategy for treating breast cancer harboring wt p53 PMID: 26181202
- MDM4 overexpression is related to complex karyotype-acute myeloid leukemia with wild-type TP53 and might play a pathogenic role by inhibiting p53-signal pathway. PMID: 25405759
- MDMX exerts oncogenic activity via suppression of RB. PMID: 25703327
- We show using reporter gene assays and endogenous MDM4 expression analyses that miR-191-5p and miR-887 have a specific affinity for the rs4245739 SNP C-allele in prostate cancer PMID: 25670033
- MDM4 mutation identified in a glioma patient was associated with loss of the putative MDM4 target site. Therefore, let-7 binding to MDM4 is implicated in the DNA damage response PMID: 26028311
- Finally, a strong association between the expression of EEF1A2, phosphorylated AKT and MDM4 was observed in human HCC samples. Strong activation of the EEF1A2/PI3K/AKT/mTOR/MDM4 signaling pathway was observed in HCC patients. PMID: 25394965
- Confirmation that the residue Tyr99 in MDMX can generate a steric clash with the inhibitors due to energy and structure. PMID: 22408446
- The HDMX polymorphism is unlikely to contribute to individual susceptibility to sarcoma. PMID: 24972690
- The results indicate a putative role for the MDM4 gene in predicting local recurrence of bladder cancer. PMID: 25026175
- Endogenously high levels of Mdm4 inhibit and sequester p53 in AML. High levels of Mdm4 do not block function of Mdm2 inhibitors in AML. PMID: 24659749
- in the absence of p53 or in the presence of MdmX overexpression, FL118 promotes p53-independent apoptosis PMID: 25512388
- Downregulation of Mdm4 by miR-661 augments p53 activity and inhibits cell cycle progression in p53-proficient cells. PMID: 24141721
- Loss of MDM4 expression is associated with glioblastoma. PMID: 24445145
- the novel variant MDM4-B may play a role in glioma tumorigenesis or cancer progression PMID: 23994448
- The activation level of the EEF1A2/PI3K/AKT/mTOR/MDM4 axis significant influences the survival probability of hepatocellular carcinoma patients. PMID: 24285179
- Functional MDM4 rs4245739 SNP, alone and in combination with P53 Arg72Pro genetic variant, was associated with a significantly decreased risk of breast cancer in Chinese populations. PMID: 23793604
- MDMX contains a regulatory element (the "WWW element") that binds to its own N-terminal domain and prevents MDMX from binding to p53. PMID: 24127580
- The MDM4 rs4245739 (miR-191 target site) AC and CC genotypes were significantly associated with decreased esophageal squamous cell carcinoma risk PMID: 23724042
- Mdm4 is upregulated in a substantial proportion of stage I-IV human melanomas. It promotes the survival of metastatic melanoma by antagonizing p53. In xenografts, inhibition of the MDM4-p53 interaction restored p53 function. PMID: 22820643
- The interaction of nutlin with MDMX is very short-lived compared with MDM2 and does not show such direct initial interactions with the binding site. PMID: 23324352
- The rs1563828(C > T) polymorphism in MDM4 gene may not confer risk to breast cancer, especially for early-onset breast cancer patients. Homozygous TT of rs1563828 is associated with younger age of onset of breast cancer. PMID: 22490292
- FULL length-MDM4 and a splicing variant of MDM4 overexpression are indicators of p53 aberrations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients, suggesting that those patients have a poor prognosis. PMID: 22937789
- MicroRNA-34a modulates MDM4 expression via a target site in the open reading frame. PMID: 22870278
- The results of this study showed that strong association between MDM4 gene alternation and high-grade oligodendroglial tumors. PMID: 22825724
- DNA damage activates p53 in part by disrupting CK1a-MDMX interaction and reducing MDMX-p53 binding affinity. PMID: 23028042
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:MDM2/MDM4 family
-
組織特異性:Expressed in all tissues tested with high levels in thymus.
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Mouse GDNF family receptor alpha-like (Gfral), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human R-spondin-1 (RSPO1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Dog Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
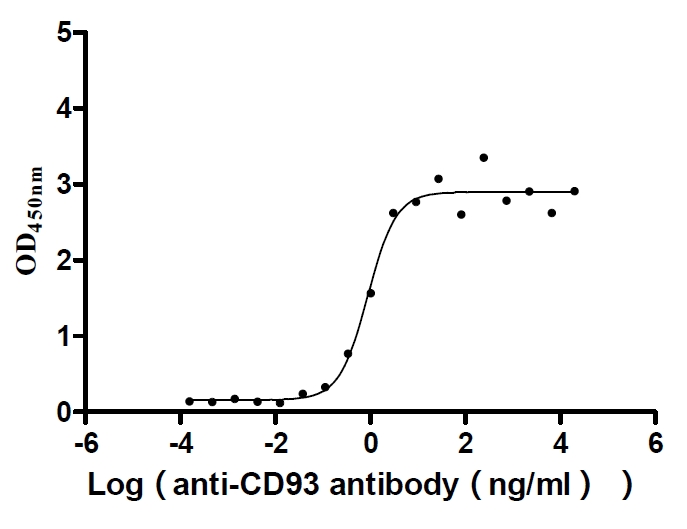
Recombinant Human Complement component C1q receptor (CD93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
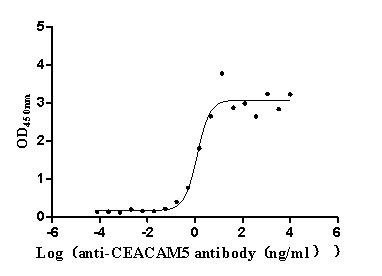
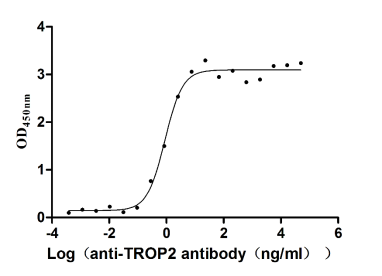
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
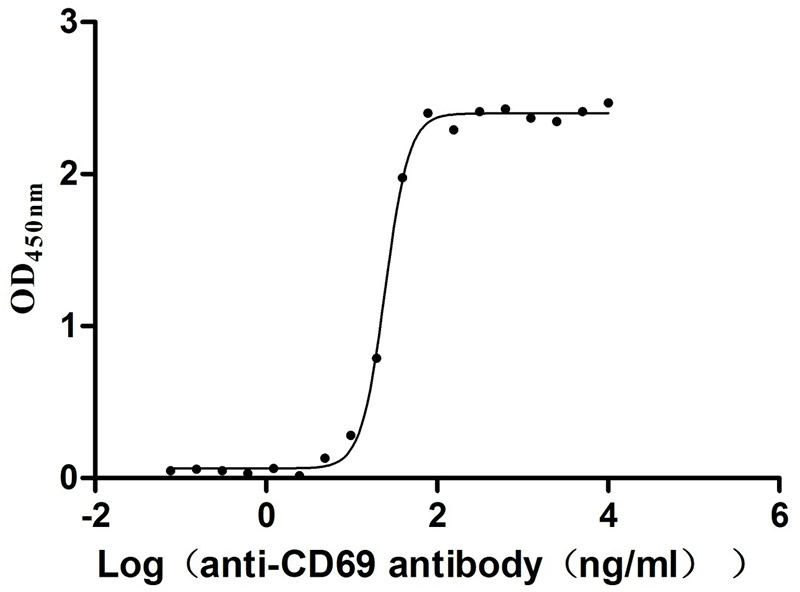
Recombinant Human Early activation antigen CD69 (CD69), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)




-AC1.jpg)