Recombinant Mouse Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1D (Cacna1d), partial
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Mouse Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1D (Cacna1d), partial
-
貨號(hào):CSB-EP860754MO
-
規(guī)格:¥2328
-
圖片:
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
純度:Greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
生物活性:Not Test
-
基因名:Cacna1d
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Calcium channel, L type, alpha-1 polypeptide isoform 2;Voltage-gated calcium channel subunit alpha Cav1.3
-
種屬:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白長(zhǎng)度:Partial
-
來源:E.coli
-
分子量:83.7 kDa
-
表達(dá)區(qū)域:1644-2144aa
-
氨基酸序列EQGLVGKYPAKNTTIALQAGLRTLHDIGPEIRRAISCDLQDDEPEDSKPEEEDVFKRNGALLGNHVNHVNSDRRDSLQQTNTTHRPLHVQRPSMPPASDTEKPLFPPAGNSGCHNHHNHNSIGKQAPTSTNANLNNANMSKAAHGKPPSIGNLEHVSENGHYSCKHDRELQRRSSIKRTRYYETYIRSESGDEQFPTICREDPEIHGYFRDPRCLGEQEYFSSEECCEDDSSPTWSRQNYNYYNRYPGSSMDFERPRGYHHPQGFLEDDDSPTGYDSRRSPRRRLLPPTPPSHRRSSFNFECLRRQSSQDDVLPSPALPHRAALPLHLMQQQIMAVAGLDSSKAQKYSPSHSTRSWATPPATPPYRDWSPCYTPLIQVDRSESMDQVNGSLPSLHRSSWYTDEPDISYRTFTPASLTVPSSFRNKNSDKQRSADSLVEAVLISEGLGRYARDPKFVSATKHEIADACDLTIDEMESAASTLLNGSVCPRANGDMGPISHRQ
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白標(biāo)簽:C-terminal GFP-tagged
-
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
緩沖液:If the delivery form is liquid, the default storage buffer is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 5%-50% glycerol. If the delivery form is lyophilized powder, the buffer before lyophilization is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose.
-
復(fù)溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:Voltage-sensitive calcium channels (VSCC) mediate the entry of calcium ions into excitable cells and are also involved in a variety of calcium-dependent processes, including muscle contraction, hormone or neurotransmitter release, gene expression, cell motility, cell division and cell death. The isoform alpha-1D gives rise to L-type calcium currents. Long-lasting (L-type) calcium channels belong to the 'high-voltage activated' (HVA) group. They are blocked by dihydropyridines (DHP), phenylalkylamines, and by benzothiazepines.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- The results signify a developmental decline in the sensitivity of CDI to global elevations in Ca ( 2+) , which restricts negative feedback regulation of Cav 1.3 channels to incoming Ca ( 2+) ions in mature inner hair cells (IHCs). PMID: 23510940
- Ventral tegmental area Cav1.3 channel activation robustly mediates cocaine-related, depression-related and social behavior via distinct nucleus accumbens AMPAR mechanisms with no effect on anxiety-like behavior. PMID: 28194001
- findings suggest a key role of CaV1.3 in regulating dendritic spine structure. Under physiological conditions it may contribute to the structural plasticity of glutamatergic synapses. Conversely, altered regulation of CaV1.3 channels may provide an important mechanism in the development of postsynaptic aberrations associated with neurodegenerative disorders. PMID: 27708393
- These results provide the evidence of a direct regulatory role of Snapin on Cav1.3 channels in atrial myocytes. PMID: 27915047
- Ca(2+) entry serves critical cellular functions in virtually every cell type, and appropriate regulation of Ca(2+) in neurons is essential for proper function. PMID: 28258168
- Auditory inner hair cells (IHCs) encode sounds into nerve impulses through fast and indefatigable Ca(2+)-dependent exocytosis at their ribbon synapses. We show that this synaptic process involves long and short C-terminal isoforms of the Cav1.3 Ca(2+) channel that differ in the kinetics of their Ca(2+)-dependent inactivation and their relative sensitivity to the l-type Ca(2+) channel blocker nifedipine. PMID: 28193694
- Inner hair cells possess calcium channels that are essential for transmitting sound information into synaptic transmitter release. Voltage-gated calcium channels can coassemble with auxiliary subunit alpha2delta isoforms 1-4. We found that hair cells of the mouse express the auxiliary subunit alpha2delta2, which is needed for normal hearing thresholds. Using a mouse model with a mutant, nonfunctional alpha2delta2 prote... PMID: 27798183
- alpha1D Ca and SK4 channels are coupled in the atria, and deletion of alpha1D leads to decreased SK4 mRNA and BNP secretion providing evidence for a novel role of alpha1D in atrial endocrine function PMID: 27884747
- beta-Adrenergic stimulation enhanced pacemaking of both genotypes, though, Cav1.3(-/-) sino-atrial node cells remained slower than wild type PMID: 26786159
- implicating Cav1.3 as an essential element for hippocampus-associated cognitive functions PMID: 26459417
- Studies indicate the function of L-type calcium channels Cav1.3 in chromaffin cells. PMID: 25966692
- Data suggest that the ion channels CaV1.3, bestrophin-1 and maxiK were identified as players in the regulation of photoreceptor outer segments (POS) phagocytosis by the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). PMID: 26427483
- RIM2alpha and RIM2beta promote a large complement of synaptic CaV1.3 Ca(2+) channels at inner hair cell presynaptic active zones and are required for normal hearing. PMID: 26034270
- Results indicate that the Cav1.3 subtype is crucial to regulation of basal single-spike firing, while activation of both Cav1.2 and Cav1.3 can support burst firing of dopaminergic VTA neurons. PMID: 24848473
- ablation of Cav1.3 results in a decrease in the protein expression of myosin light chain 2, which interacts and increases the membrane localization of SK2 channels. PMID: 25538241
- Cav1.3 significantly upregulated in brain 24hr after single nicotine injection; Cav1.2 expression was not significantly altered; downregulation of Cav1.2 24hr after chronic nicotine administration; strong upregulation of Cav1.2 following 7-day abstinence PMID: 24470632
- CaV1.3(-/-) RPE lacked peak phagocytic activity following morning photoreceptor shedding in wild-type RPE and retained a higher number of phagosomes at a later time of day. PMID: 24407175
- (Cav1.3) The key yet differential roles of Cav1.2 and Cav1.3 channels mediate action potential firing and exocytotic events in the neuroendocrine chromaffin cell. PMID: 21054386
- Cav3.2 channels support dilatation of efferent arterioles and affect glomerular filtration rate, whereas Cav3.1 channels in vivo contribute to renal vascular resistance. PMID: 24966091
- The co-localization of Ca(v)1.3 and CB in certain brain regions such as the hippocampus suggests their important roles in neuroplasticity. PMID: 24394909
- Ca(v)1.3.3 calcium channel is a good target for prevention and therapy of age-related hearing loss PMID: 23470431
- Report role of Cav1.3 in controlling sinus rhythm. PMID: 23045342
- A Cav1.3-dependent mechanism is demonstrated through which both inhibitory circuit formation and determination of the neurotransmitter phenotype are achieved. PMID: 23077046
- The role of the peripheral deafness gene Cacna1d, was assessed. PMID: 22678062
- Findings indicated that the LTCC alpha(1D) subunit located on the ER membrane has a novel function as a gatekeeper for the Zn wave, which is involved in regulating NF-kappaB signaling and the delayed-type allergic reaction. PMID: 22745805
- our results neurochemically corroborate the robustness of the nigrostriatal DA neurons in the absence of Ca(v)1.3 channels, but suggest that complete deletion of this channel affected a variety of other transmitter systems PMID: 22202668
- analysis of functional characterization of alternative splicing in the C terminus of L-type CaV1.3 channels PMID: 21998309
- expression of L-VGCC alpha1D subunit found in WT hearts was abolished in clock mutant hearts, indicating that in mammalian hearts, the daily oscillations of the activities of L-VGCCs were downstream elements of cardiac core oscillators PMID: 21921295
- while Ca(v)1.3 channels are required for automaticity, Ca(v)3.1 channels are important for maximal pacing rates of mouse AVNCs. PMID: 21406960
- at potentials near resting (-50 mV), Ca(v)1.3 carries equal amounts of Ca(2+) current to Ca(v)1.2 but activates at 9 mV more negative potentials. PMID: 21406973
- The Cacna1d has been expressed in proliferating myoblasts, whereas in differentiating mononuclear myoblasts the expression of this gene was significantly decreased. PMID: 21789999
- results imply that Cav1.3 channels are indispensable for the development of the central auditory system. PMID: 21632949
- Cacna1d knockout mice are deaf and have impaired sinoatrial node function. PMID: 17650821
- Study demonstrates that the distinct biophysical properties of Ca(v)1.3 Ca(2+) channel play critical roles in the firing frequency of AV node tissues. PMID: 20951705
- L-type divalent calcium channels and their process development are in situ evidence for the influence of golli myelin basic proteins on voltage-operated channels, offering an explanation for the hypomyelination observed in golli-deficient mouse brains. PMID: 20607717
- findings indicate that CaV1.3 L-type Ca2+ channels modulate depression-like behaviour but are not essential for visual function. PMID: 19664321
- besides presumably reduced synaptic bodies the absence of class D L-type Ca(2+) channels does not prevent morphological development of the cochlea until postnatal day but may cause cochlear degeneration thereafter PMID: 12684182
- In outer hair cells from Cav1.3 deficient mice, Ba2+ current density was reduced to 0.6 +/- 0.5 pA pF-1 (n = 9) indicating that > 97 % of the Ca2+ channel current in OHCs flows through Cav1.3 PMID: 14514878
- Cav 1.3 (alpha1D) L-type Ca2+ channel in mouse is expressed in the liver PMID: 15010858
- During development, Ca(v)1.3 immunoreactivity was observed in the cochlea as early as embryonic day 15, with expression increasing at birth. PMID: 15158080
- In contrast to impaired hearing, alpha1D-/- mice have balance performances equivalent to their wild-type littermates PMID: 15357422
- D2 dopaminergic & M1 muscarinic receptors selectively modulate CaV1.3 in striatal medium spiny neurons. The splice variant in these cells has cytoplasmic Src homology 3 and PDZ-95/Discs large/ZO-1 domains that bind Shank. PMID: 15689540
- We established the differential distribution of Cav1.3 Ca2+ channels in atrial myocytes compared with ventricles. Our data represent the first report demonstrating important functional roles for Cav1.3 Ca2+ channel in atrial tissues. PMID: 16172271
- Cav1.3 knockout mice exhibit significant impairments in consolidation of contextual fear conditioning. Overtrained KO mice exhibit normal rates of extinction. Cav1.3 knockout mice perform normally on the hidden platform version of the Morris water maze. PMID: 17015855
- In conclusion, our results find that amphetamine increases D(2)L mRNA expression in the dStr and the VTA, an adaptation that correlates with expression of sensitized behavior and dependence on Ca(v)1.3 Ca(2+) channels. PMID: 17026527
- Voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels Cav1 .2 and Cav1.3 are the predominant brain l-type calcium channels PMID: 17052224
- alternative splicing of alpha1 1.3 may influence activity-dependent regulation of Ca(v)1.3 channels at the synapse PMID: 17287512
- Our results identify Ca(V)1.3 as the principal pore-forming subunit of VDCCs involved in stimulating the ERG LP. PMID: 17376851
- L-type calcium channel Ca(v)1.3 (alpha1D) subunit mRNA in rods indicates it may be component of channels mediating residual photoreceptor responses observed in mutant mice lacking functional Ca(v)1.4 (alpha1F) subunits and in humans with CSNB2. PMID: 17563731
- The L-type channel Ca(v)1.3 protein significantly decreased upon chronic morphine treatment. PMID: 18048029
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Calcium channel alpha-1 subunit (TC 1.A.1.11) family, CACNA1D subfamily
-
組織特異性:Expressed in the inner hair cells (IHC) of the cochlea.
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 Spike glycoprotein (S), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (2019-nCoV) (SARS-CoV-2)
-
Recombinant Human T-cell antigen CD7 (CD7), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 8 (TNFSF8), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
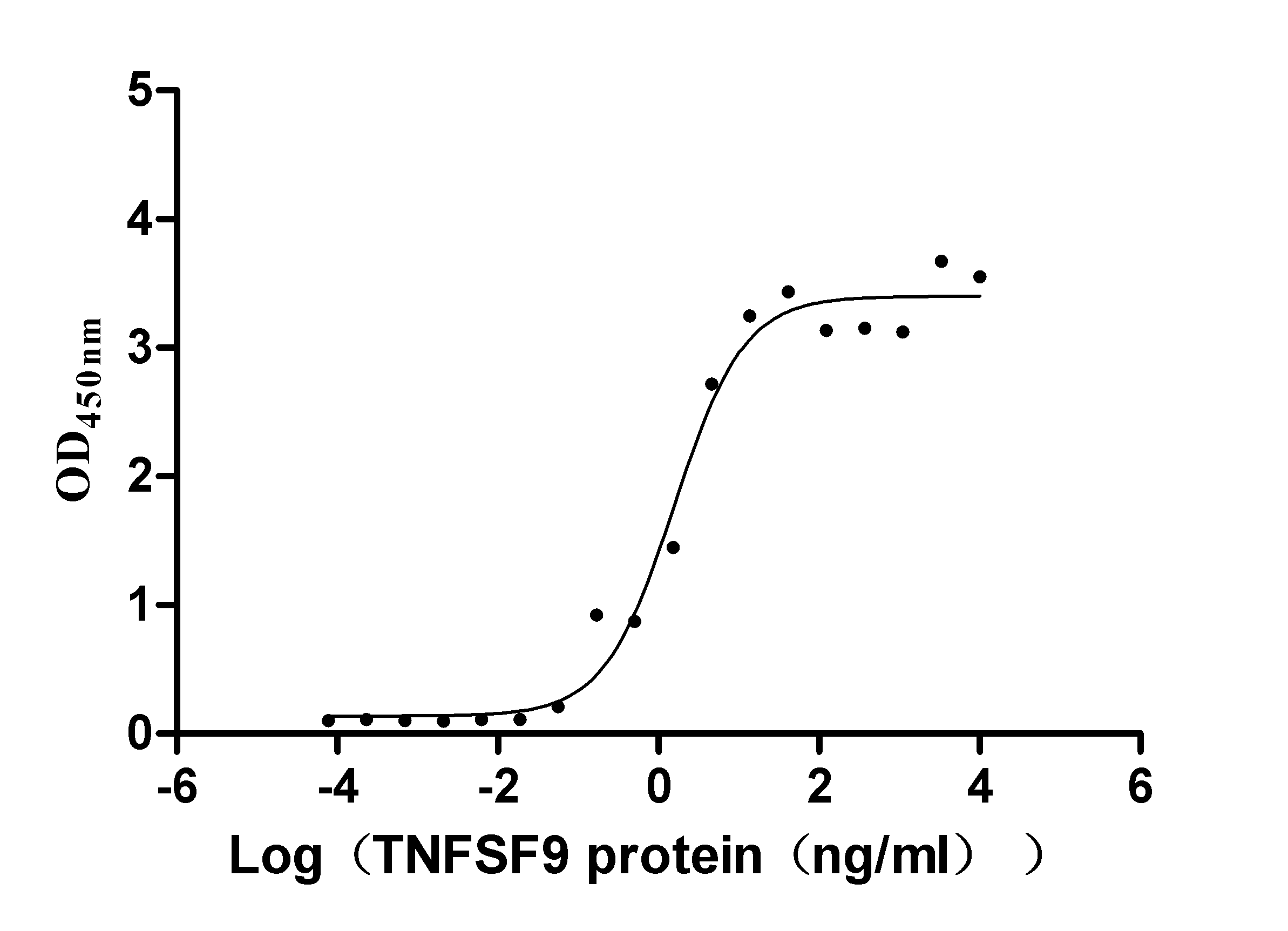
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 9 (TNFRSF9), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
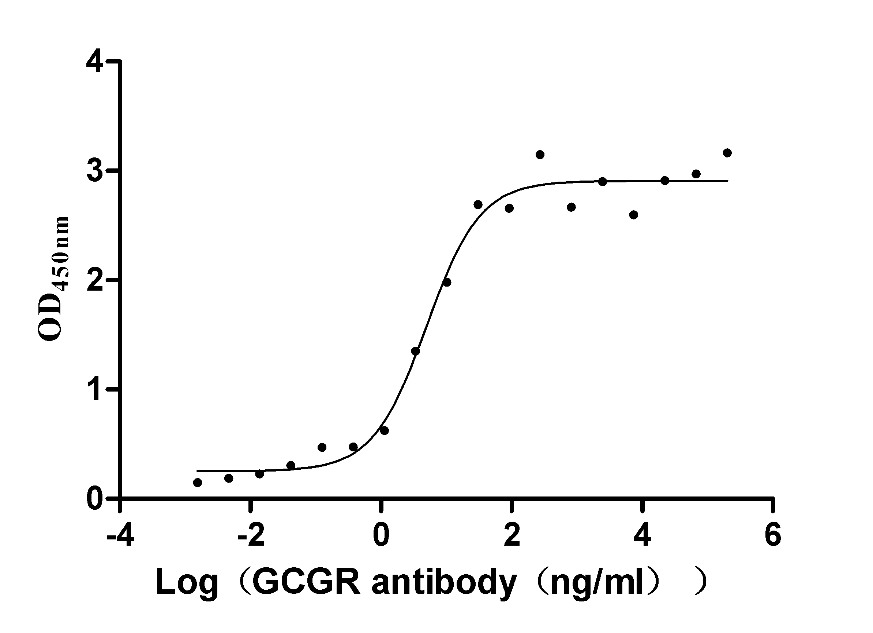
Recombinant Human Glucagon receptor (GCGR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
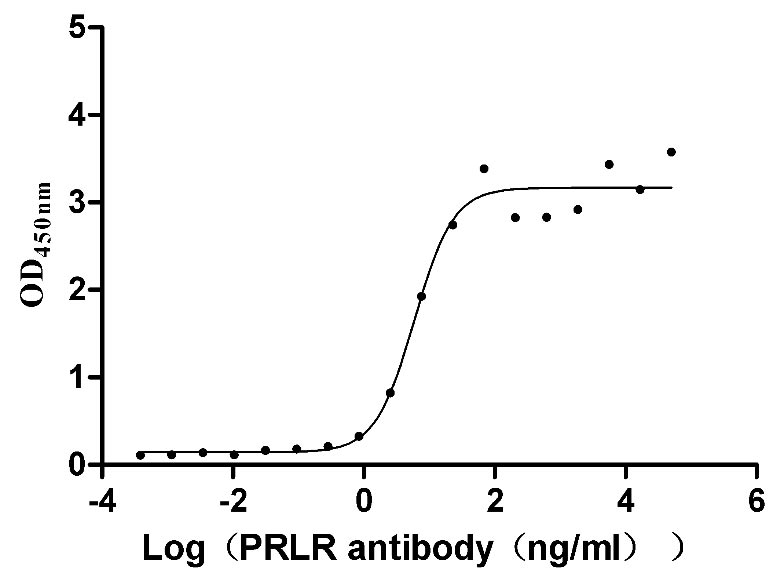
Recombinant Mouse Prolactin receptor (Prlr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
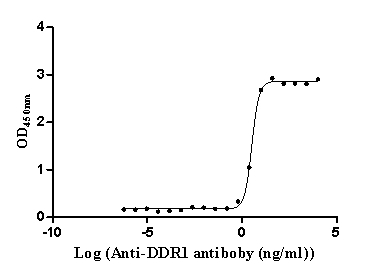
Recombinant Human Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 (DDR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Mucin-17 (MUC17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)