Recombinant Mouse Transforming protein RhoA (Rhoa)
-
中文名稱:小鼠Rhoa重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-YP865565MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Rhoa重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP865565MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Rhoa重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP865565MO-B
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Rhoa重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-BP865565MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Rhoa重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-MP865565MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Rhoa
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Rhoa; Arha; Arha2; Transforming protein RhoA; EC 3.6.5.2
-
種屬:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白長度:full length protein
-
表達區(qū)域:1-190
-
氨基酸序列MAAIRKKLVI VGDGACGKTC LLIVFSKDQF PEVYVPTVFE NYVADIEVDG KQVELALWDT AGQEDYDRLR PLSYPDTDVI LMCFSIDSPD SLENIPEKWT PEVKHFCPNV PIILVGNKKD LRNDEHTRRE LAKMKQEPVK PEEGRDMANR IGAFGYMECS AKTKDGVREV FEMATRAALQ ARRGKKKSGC
-
蛋白標簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復(fù)溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶點詳情
-
功能:Small GTPase which cycles between an active GTP-bound and an inactive GDP-bound state. Mainly associated with cytoskeleton organization, in active state binds to a variety of effector proteins to regulate cellular responses such as cytoskeletal dynamics, cell migration and cell cycle. Regulates a signal transduction pathway linking plasma membrane receptors to the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers. Involved in a microtubule-dependent signal that is required for the myosin contractile ring formation during cell cycle cytokinesis. Plays an essential role in cleavage furrow formation. Required for the apical junction formation of keratinocyte cell-cell adhesion. Essential for the SPATA13-mediated regulation of cell migration and adhesion assembly and disassembly. The MEMO1-RHOA-DIAPH1 signaling pathway plays an important role in ERBB2-dependent stabilization of microtubules at the cell cortex. It controls the localization of APC and CLASP2 to the cell membrane, via the regulation of GSK3B activity. In turn, membrane-bound APC allows the localization of the MACF1 to the cell membrane, which is required for microtubule capture and stabilization. Regulates KCNA2 potassium channel activity by reducing its location at the cell surface in response to CHRM1 activation; promotes KCNA2 endocytosis. Acts as an allosteric activator of guanine nucleotide exchange factor ECT2 by binding in its activated GTP-bound form to the PH domain of ECT2 which stimulates the release of PH inhibition and promotes the binding of substrate RHOA to the ECT2 catalytic center. May be an activator of PLCE1. In neurons, involved in the inhibiton of the initial spine growth. Upon activation by CaMKII, modulates dendritic spine structural plasticity by relaying CaMKII transient activation to synapse-specific, long-term signaling. Acts as a regulator of platelet alpha-granule release during activation and aggregation of platelets.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- KLF4 indirectly modulates the actin cytoskeleton morphology via activity of RhoA in order to inhibit cellular migration and invasion. PMID: 29498307
- Cdc42 and RhoA act as a regulatory circuit downstream of the megakaryocytes -specific mechanoreceptor GPIb to coordinate polarized transendothelial platelet biogenesis. PMID: 28643773
- Non-visual arrestins regulate the focal adhesion formation via small GTPases RhoA and Rac1 independently of G-protein-coupled receptors. PMID: 29133163
- RHOA loss reduces YAP signaling of the Hippo pathway and affects YAP effector epiregulin (EREG) expression in the crypts. Expression of an active YAP (S112A) mutant rescues ntestinal stem cells (ISCs) marker expression, ISC regeneration, and ISC-associated Wnt signaling, but not defective epithelial polarity, in RhoA knockout mice, implicating YAP in RHOA-regulated ISC function. PMID: 29129684
- GTP-RhoA and ROCK1 expression levels were markedly increased in a time-dependent manner in the ears and lungs of mice treated with penicillin. PMID: 27619816
- Tyr42 phosphorylation of RhoA GTPase promotes tumorigenesis through NF-kappaB. PMID: 28712859
- RhoA modulates the choices of molar cuspal shape by coordinating adhesion junctions, actin distribution, and fibronectin localization to drive inner dental epithelium invagination. PMID: 27892530
- Kctd13 deletion reduces synaptic transmission, which correlates with increased levels of RhoA, a KCTD13/CUL3 ubiquitin ligase substrate PMID: 29088697
- Crmp4(-/-) OBs exhibited enhanced activation of RhoA/focal adhesion kinase (FAK) signaling that led to cytoskeletal changes with increased cell spreading. PMID: 28019696
- Codepletion of the actomyosin regulator RhoA and Afadin results in defects in the central lumens and arrests lumen remodeling PMID: 29330353
- Hydrogen peroxide oxidizes RhoA at Cys16 and Cys20, and activates RhoA via Vav2. PMID: 27974245
- These results reveal a novel signaling network, the Sema4D-RhoA-Akt signal cascade, that coordinates cellular function and morphology and highlights the importance of specific spatiotemporally restricted components of a signaling pathway in the regulation of ameloblast differentiation. PMID: 27218883
- RhoA deficiency could disrupt podocyte cytoskeleton and induce podocyte apoptosis by inhibiting YAP/dendrin signal. PMID: 27389190
- These results suggested that, in addition to inhibiting Noggin transcription, RhoA activity in wild-type murine embryonic stem cells also prevented neural differentiation by limiting Noggin secretion. PMID: 27460990
- Rho attenuates the interaction between Amot and Nf2 by binding to the coiled-coil domain of Amot. PMID: 28947533
- we uncovered cell state plasticity and adhesion dynamics regulated by Ror2, which influenced Ras Homology Family Member A (RhoA) and Rho-Associated Coiled-Coil Kinase 1 (ROCK1) activity downstream of Dishevelled-2 (Dvl2). PMID: 28650466
- Active Rho-kinase diffuses to growing other immature neurites and inhibits their outgrowth to ensure single axon formation. PMID: 28652571
- Data indicate that oxidative stress in diabetes causes a decrease in miR-133a expression leading to an increase in RhoA/Rho kinase pathway and muscle contraction. PMID: 28678840
- Downregulation of Cul3 led to a marked increase in RhoA protein expression after 6 days of adipocytes differentiation, suggesting that Cul3 is involved in the regulation of RhoA stability. PMID: 28499918
- Impaired denitrosylation is associated with detrusor overactivity, which is linked with upregulated RhoA/Rho-kinase signalling PMID: 28303627
- The in vivo function of RhoA in corpus luteum (CL) luteal cell cytoskeleton integrity, cholesterol transport, StAR expression, and progesterone synthesis, and a positive feedback on StAR expression in CL by progesterone signaling. PMID: 28498971
- Reveal novel intracellular signaling mechanisms involving RhoA/STAT3 underlying the contribution of reactive astrocyte dynamics to glial scar formation. PMID: 28642362
- P311 could accelerate skin wound reepithelialization by promoting the migration of Epidermal Stem Cell through RhoA and Rac1 activation. PMID: 27927130
- We show that RhoA mRNA levels were significantly higher compared with the RhoB mRNA levels in ESCs as well in various cancer cell lines and this difference could be accounted for by differences in the activities of the corresponding promoters. PMID: 28739254
- Results strongly support the hypothesis that spinal RhoA/ROCK signaling plays a central role in the neuropathic pain. In addition, simvastatin might exert its antihyperalgesic and antiallodynic effects through the attenuation of sensitization of spinal nociceptive transmission that is modulated by mechanisms dependent on the RhoA/ROCK signaling. PMID: 27457035
- Findings suggest that atorvastatin attenuates diabetes-associated renal injury by reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, RhoA activity and normalizing Akt/GSK3beta signaling pathways. PMID: 27649495
- findings describe a novel RhoA regulatory mechanism. PMID: 27992599
- ANXA1 restores Abeta42-induced blood brain barrier disruption through inhibition of RhoA-ROCK signaling pathway PMID: 27633771
- study delineates a mechanism in which NCAM promotes ephrin-A5-dependent clustering of EphA3 through interaction of the NCAM Ig2 domain and the EphA3 CRD, stimulating EphA3 autophosphorylation and RhoA signaling necessary for growth cone repulsion in GABAergic interneurons in vitro, which may extend to remodeling of axonal terminals of interneurons in vivo. PMID: 27803162
- M0 and M2 macrophages have a radically different phenotype and polarity from M1 macrophages, and that this is mirrored in dissonant response to RhoA pathway interference. PMID: 27628094
- the cross-talk between canonical and non-canonical signaling pathways of Wnt3A, which induces GSK-3beta phosphorylation and beta-catenin accumulation through RhoA and ROCK activation. PMID: 27575935
- these findings reveal that Arhgef1 functions as a negative regulator of neurite outgrowth through regulating RhoA-cofilin pathway and actin dynamics. PMID: 27489999
- presentation of a form of biochemical computation in dendrites involving the controlled complementation of three molecules--Rac1, RhoA and Cdc42--that simultaneously ensures signal specificity and primes the system for BDNF-dependent homo- and heterosynaptic plasticity PMID: 27680697
- The transcriptional co-activator MRTF-A was activated by sphingosine-1-phosphate as assessed by its nuclear accumulation and induction of a RhoA/MRTF-A luciferase reporter. PMID: 27094722
- In conclusion, these results indicate the sub-chronic ethanol treatment decreased the expression of RhoA in mouse corpus cavernosum PMID: 26728616
- RhoA-PLD1 signaling is involved in acidic extracellular pH-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 in mouse metastatic B16-BL6 melanoma cells PMID: 26782071
- Caspase-11 targets cofilin via the RhoA GTPase, whereas caspase-1 engages the Slingshot phosphatase PMID: 26686473
- RhoA determines lineage fate of mesenchymal stem cells by modulating CTGF-VEGF complex in extracellular matrix. PMID: 27126736
- TcdB proteins target Rac, Cdc42, Rap, and R-Ras and glucosylates RhoA. PMID: 26755157
- In cultured neonatal cardiac fibroblasts, p63RhoGEF regulated the angiotensin II (Ang II)-dependent RhoA activation, the activation of the serum response factor, and the expression and secretion of CTGF. PMID: 26392029
- Inhibition of the RhoA/Rock2 kinase pathway prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced hyperalgesia and the release of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta in the mouse spinal cord. PMID: 26416580
- indicates that the up-regulation of ROCK1 activity in RhoA-deleted macrophages and macrophage phenotype/polarity are dependent on non-apoptotic Caspase-3 and are sensitive to Caspase-3 inhibition PMID: 26875770
- These findings uncover deficient prenylation of Rho-A as a key player in the pathogenesis of IBDs. PMID: 26752649
- In summary, the dihydroxycoumarin derivative daphnetin inhibits the invasion and migration of LM8 cells, and therefore represents a promising agent for use against metastatic cancer. PMID: 26845352
- Spindle organization and actin assembly are regulated through a RhoA-FMNL1-GM130 pathway in oocyte meiosis. PMID: 26083584
- The results provide a starting point to dissect spatiotemporal Rhoa GTPase signaling networks that regulate neurite outgrowth. PMID: 26728857
- Soluble beta-amyloid disrupts actin and microtubule dynamics via activation of RhoA and inhibition of histone deacetylase 6 in cultured hippocampal neurons. PMID: 26198811
- A very rapid reduction in p27-phospho-Ser10 levels at the onset of atherogenesis, which contributes to early plaque build-up through RhoA/ROCK-induced integrin expression, is reported. PMID: 25908026
- Findings indicate GTPase RhoA as a central regulator of dendritic cells (DCs) homeostasis. PMID: 26408665
- Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP)-interacting protein (WIP) as a novel component of neuronal synapses whose absence increases dendritic spine size and filamentous actin levels in an N-WASP/Arp2/3-independent, RhoA/ROCK/profilinIIa-dependent manner. PMID: 24698977
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Cell membrane; Lipid-anchor; Cytoplasmic side. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Cleavage furrow. Cytoplasm, cell cortex. Midbody. Cell projection, lamellipodium. Cell projection, dendrite.
-
蛋白家族:Small GTPase superfamily, Rho family
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human SARS coronavirus Spike glycoprotein (S), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Human SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV) (Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus)
-
Recombinant Human Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-3 (ERBB3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Cell adhesion molecule 1 (CADM1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
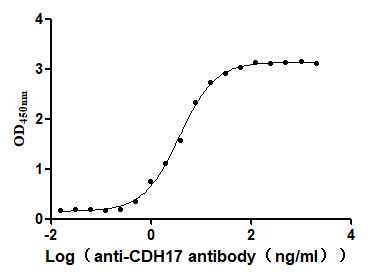
Recombinant Human Cadherin-17 (CDH17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
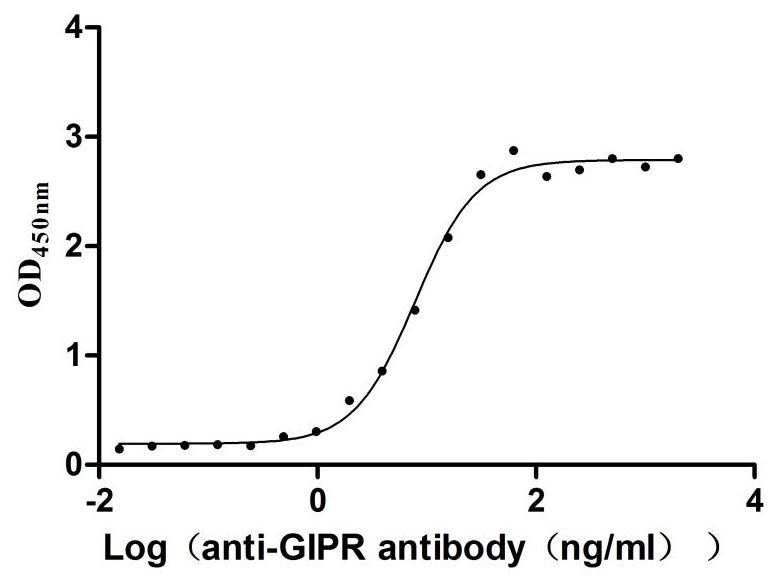
Recombinant Rat Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (Gipr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
-
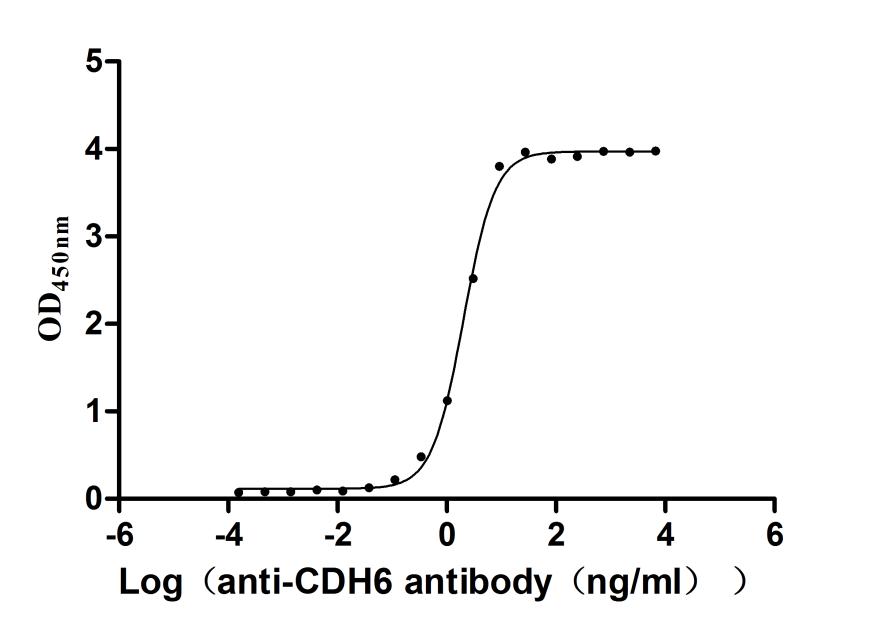
Recombinant Mouse Cadherin-6(Cdh6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)



-AC1.jpg)