Recombinant Mouse Apelin receptor (Aplnr), partial
-
中文名稱:
-
貨號(hào):CSB-EP001910MO1
-
規(guī)格:¥2328
-
圖片:
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
純度:Greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:Aplnr
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Aplnr; Agtrl1; Apj; Apelin receptor; Angiotensin receptor-like 1; G-protein coupled receptor APJ; MSR
-
種屬:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白長度:Partial
-
來源:E.coli
-
分子量:15.1 kDa
-
表達(dá)區(qū)域:307-377aa
-
氨基酸序列YAFFDPRFRQACTSMLCCDQSGCKGTPHSSSAEKSASYSSGHSQGPGPNMGKGGEQMHEKSIPYSQETLVD
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白標(biāo)簽:N-terminal 10xHis-tagged and C-terminal Myc-tagged
-
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
緩沖液:If the delivery form is liquid, the default storage buffer is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 5%-50% glycerol. If the delivery form is lyophilized powder, the buffer before lyophilization is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose.
-
復(fù)溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20°C/-80°C. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:13-23 business days
-
注意事項(xiàng):Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:Receptor for apelin receptor early endogenous ligand (APELA) and apelin (APLN) hormones coupled to G proteins that inhibit adenylate cyclase activity. Plays a key role in early development such as gastrulation, blood vessels formation and heart morphogenesis by acting as a receptor for APELA hormone. May promote angioblast migration toward the embryonic midline, i.e. the position of the future vessel formation, during vasculogenesis. Promotes sinus venosus (SV)-derived endothelial cells migration into the developing heart to promote coronary blood vessel development. Plays also a role in various processes in adults such as regulation of blood vessel formation, blood pressure, heart contractility and heart failure.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- the expression of APLNR (APJ/AGTRL1), the only known receptor for apelin, is predominantly restricted to the endothelial cells. PMID: 28904225
- The ELA-APJ axis protects from pressure overload-induced heart failure possibly via suppression of ACE expression and pathogenic angiotensin II signaling. PMID: 28371822
- Internalization does not appear to contribute to the desensitization of APJ-mediated ppERK1/2 activation. PMID: 27492965
- the ELABELA (ELA)-APJ signaling axis is only required for sinus venosus-derived progenitors. PMID: 28890073
- These results demonstrate a new pharmacologic property of protamine-blockade of APJ-that could explain some adverse effects observed in protamine-treated patients, and that the established antiangiogenic activity of protamine would rely on APJ antagonism. PMID: 28242772
- Apelin-36-[L28C(30kDa-PEG)] provides a starting point for the development of diabetes therapeutics that are devoid of the blood pressure effects associated with canonical APJ activation PMID: 27994053
- Results show that obese mice had significantly lower mRNA and protein expressions of apelin/ APJ in skeletal muscles than the normal body weight mice. PMID: 27834140
- These results demonstrate that overexpression of APJ in cardiomyocytes has adverse effects on cardiac function in male and non-pregnant mice and that lactation contributes to the development of postpartum cardiomyopathy in the heart with APJ overexpression. PMID: 27033703
- Endothelial CXCR4 is negatively regulated by miR-139-5p, whose transcription is in turn induced by laminar flow and APLN/APLNR signalling. PMID: 27068353
- apelin is produced by arterial endothelial cells (ECs) during embryogenesis, induces chemotaxis of venous ECs, and promotes the production of secreted Frizzled-related protein 1 by apelin receptor(+) ECs PMID: 25920569
- Findings demonstrate a stimulatory role for the islet cell apelin-APJ signaling axis in regulation of pancreatic islet homeostasis and in metabolic induced beta-cell hyperplasia. PMID: 25965959
- ERG and APLNR are essential for endothelial homeostasis in venules in the lung and that perturbation in ERG-APLNR signaling is crucial for the development of pulmonary veno-occlusive disease. PMID: 25062690
- These findings suggest that apelin-APJ signaling is a potential therapeutic target in the treatment of vasculogenic erectile dysfunction. PMID: 23578329
- regulates the Nodal/Bone Morphogenetic Protein antagonist Cerberus and the Baf60c/Smarcd3 subunit of the Brg1/Brm-associated factors (BAF) chromatin-remodelling complex PMID: 23787002
- In obese and insulin-resistant mice, plasma apelin concentration after fasting was not modified but, the gene-expression level of the APL/APJ system was augmented in the white adipose tissue and reduced in the brown adipose tissue, liver and in kidneys. PMID: 23747606
- These findings imply that the pancreatic apelin-APJ system functions to curb the inflammatory and fibrosis responses during pancreatitis, and that apelin reduces inflammation and fibrosis by reducing neutrophil recruitment and PSC activity. PMID: 23681476
- More than half of the expected Apj-/- embryos died in utero because of cardiovascular developmental defects. Apelin-APJ signaling plays a novel role as a potent regulator of endothelial MEF2 function in the developing cardiovascular system. PMID: 23603510
- Apelin-APJ signalling may promote Fas-induced liver injury at least partially via JNK activation. PMID: 23121371
- Centrally administered apelin-13 elicited depression-like behavior in mice, which was mediated via APJ receptor and kappa-opioid receptor, but not CRF receptor. PMID: 22728209
- We conclude that apelin functions as a new and potent chemoattractant for circulating cKit+/Flk1+/Aplnr+ cells during early myocardial repair, providing myocardial protection against ischemic damage by improving neovascularization via paracine action. PMID: 22753078
- study found activation of ATreceptors stimulates apelin secretion in Ca(2), protein kinase C and MAPK kinase dependent ways; activation of AT receptors inhibits apelin secretion through cAMP and cGMP dependent pathways; expression of apelin receptor is si PMID: 22249006
- data indicate that APJ is a bifunctional receptor for both mechanical stretch and the endogenous peptide apelin; by sensing the balance between these stimuli, APJ occupies a pivotal point linking sustained overload to cardiomyocyte hypertrophy PMID: 22810587
- the novel peptide apelin and its receptor APJ can induce the morphological and functional maturation of blood vessels in tumors PMID: 22037214
- Apelin receptor mRNA and apelin-13 binding site distribution in mouse tissues PMID: 22197493
- endothelial cells promote the maturation of astrocytes through the apelin/APJ system in mice PMID: 22357924
- Disruption of apelin-APJ signaling can exacerbate pulmonary hypertension mediated by decreased activation of AMP-activated kinase and eNOS. PMID: 21233449
- Apelin receptor expression by smooth muscle cells provides a paracrine pathway in injured vessels that allows endothelial-derived apelin to stimulate their division and migration into the neointima. PMID: 20176814
- Role for the apelinergic system in mechanisms controlling fluid homeostasis, particularly at a neuroendocrine level. PMID: 20136689
- data support a role for the apelin-APJ system in the regulation of smooth muscle, epithelial and goblet cell function in the GI tract PMID: 19660504
- Expression of the murine msr/apj receptor and its ligand apelin is upregulated during formation of the retinal vessels. PMID: 11744380
- APJ exerts the hypotensive effect in vivo and plays a counterregulatory role against the pressor action of angiotensin II PMID: 15087458
- Data show that the apj receptor is expressed in pancreatic islets and that apelin-36 inhibits glucose-stimulated insulin secretion both in vivo and in vitro. PMID: 15970338
- APJ/apelin-meidated molecular mechanisms for cell migration were reported. PMID: 16211245
- APJ is unlikely to be a gene causing idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy, but the independent correlation between the 212A allele and a better prognosis suggests that it might act as a modifier gene. PMID: 17826642
- The apelin-APJ system is a mediator of oxidative stress in vascular tissue, and thus we propose it to be a critical factor in atherogenesis under high-cholesterol dietary conditions. PMID: 17884970
- Involved in the regulation of blood vessel diameter during angiogenesis. PMID: 18200044
- apelin/APJ signaling pathways play a critical role in the development of the functional vascular network in adipose tissue. PMID: 18708591
- physiological role for APJ in mechanisms of water intake and fluid retention suggests an anti-diuretic effect of apelin in vivo PMID: 19578099
- Results demonstrate that endogenous apelin-APJ signaling plays a modest role in maintaining basal cardiac function in adult mice with a more substantive role during conditions of stress. PMID: 19767528
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:G-protein coupled receptor 1 family
-
組織特異性:Expressed in coronary endothelial cells (at protein level). Expressed in the embryo, allantoic and endothelial precursor cells of the yolk sac at 8 days post-coitum (dpc). Expressed in the secondary heart field and somite at 8.25 dpc. Expressed in fetal a
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
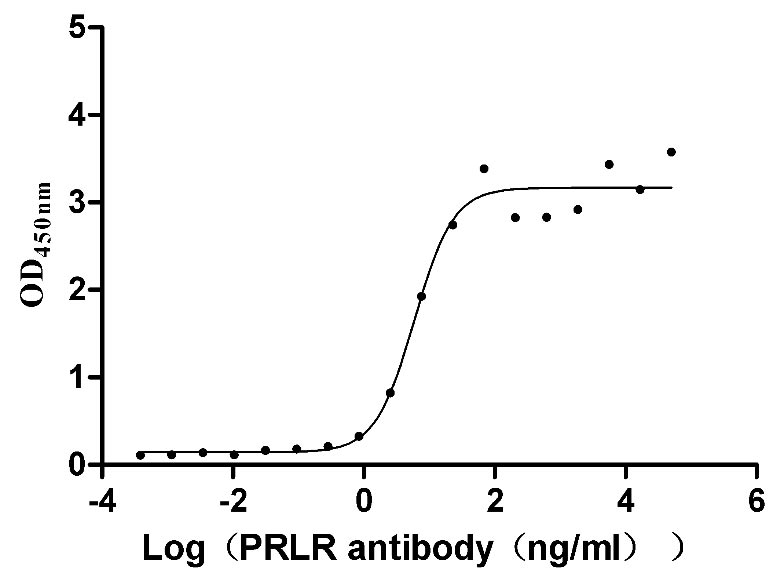
Recombinant Mouse Prolactin receptor (Prlr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Macaca mulatta Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
-
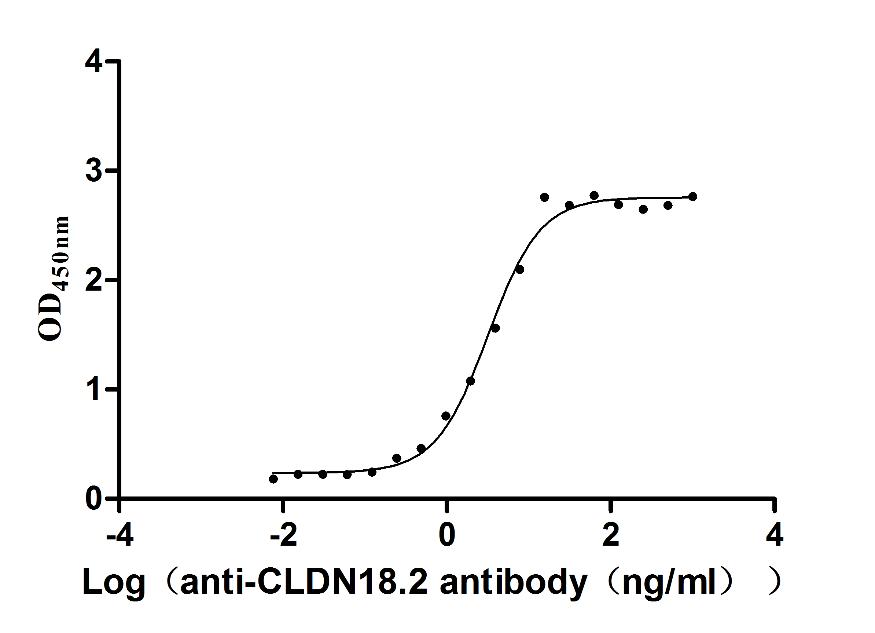
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Claudin (CLDN18)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
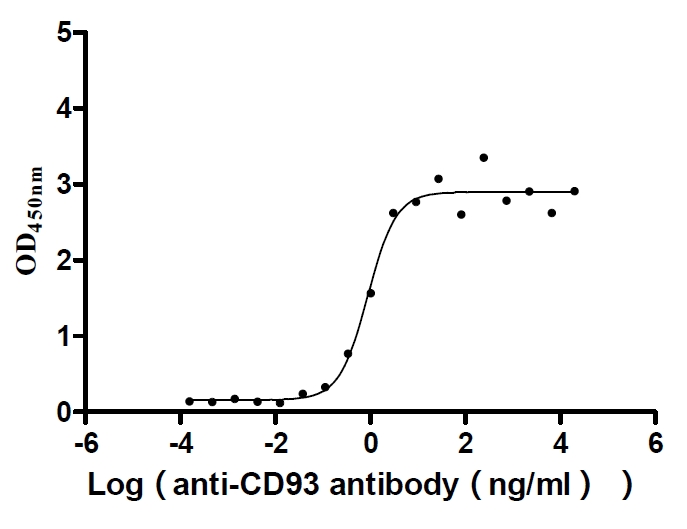
Recombinant Human Complement component C1q receptor (CD93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
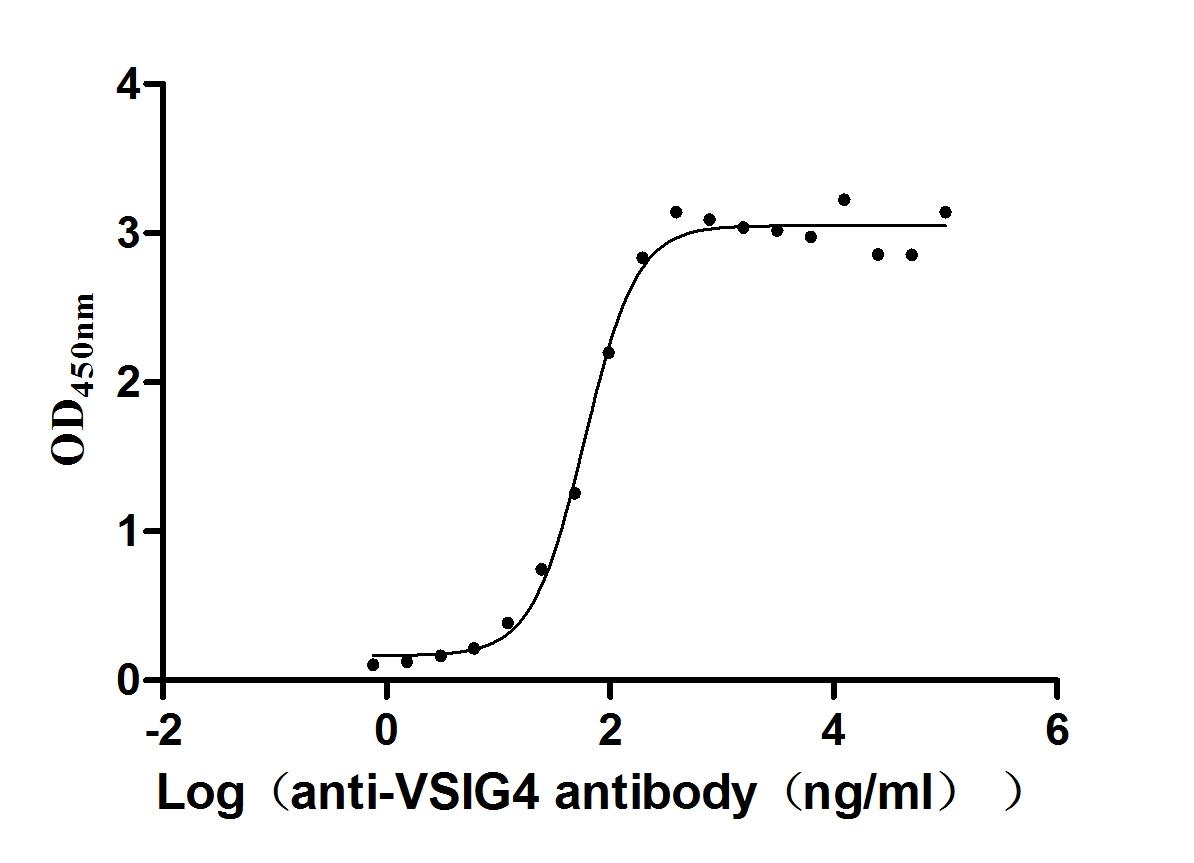
Recombinant Human V-set and immunoglobulin domain-containing protein 4 (VSIG4), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
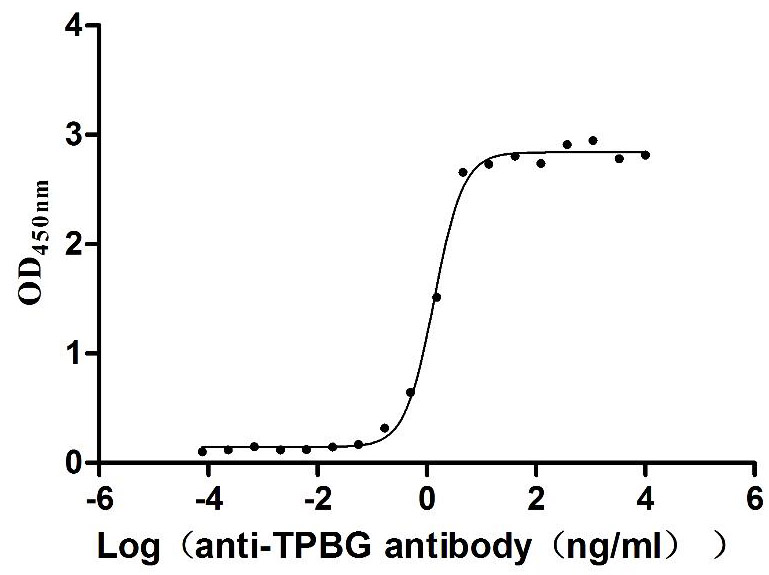
Recombinant Human Trophoblast glycoprotein (TPBG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
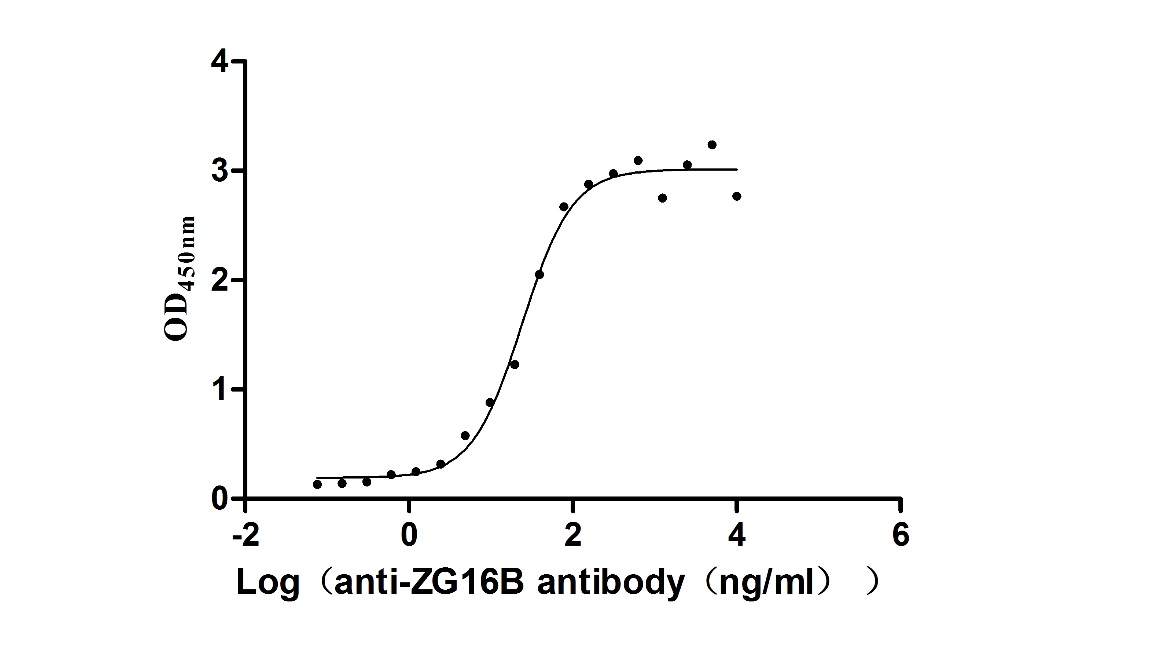
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
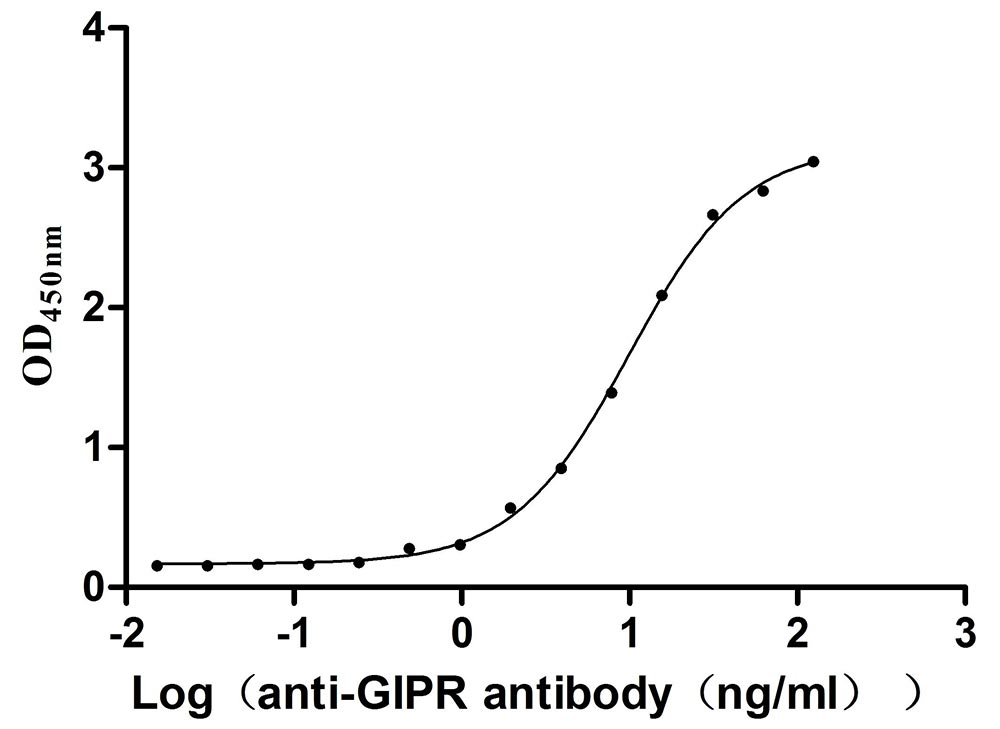
Recombinant Mouse Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (Gipr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)