Recombinant Human Protein S100-A1 (S100A1), partial
-
中文名稱:人S100A1重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-YP020622HU
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:人S100A1重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP020622HU-B
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:人S100A1重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-BP020622HU
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:人S100A1重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-MP020622HU
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Bpb; NEF; Protein S100-A1; S-100 protein alpha chain; S-100 protein subunit alpha; S100 alpha; S100 beta; S100 calcium binding protein A1; S100 calcium binding protein B; S100 calcium-binding protein A1; S100 protein alpha polypeptide; S100A; s100a1; S100B; S100beta; S10A1_HUMAN
-
種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白長度:Partial
-
表達區(qū)域:2-94
-
氨基酸序列GSELETAME TLINVFHAHS GKEGDKYKLS KKELKELLQT ELSGFLDAQK DVDAVDKVMK ELDENGDGEV DFQEYVVLVA ALTVACNNFF WENS
-
蛋白標(biāo)簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復(fù)溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Small calcium binding protein that plays important roles in several biological processes such as Ca(2+) homeostasis, chondrocyte biology and cardiomyocyte regulation. In response to an increase in intracellular Ca(2+) levels, binds calcium which triggers conformational changes. These changes allow interactions with specific target proteins and modulate their activity. Regulates a network in cardiomyocytes controlling sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) cycling and mitochondrial function through interaction with the ryanodine receptors RYR1 and RYR2, sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase/ATP2A2 and mitochondrial F1-ATPase. Facilitates diastolic Ca(2+) dissociation and myofilament mechanics in order to improve relaxation during diastole.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- Data suggest that TRPM4 exhibits binding sites for calmodulin (CaM) and S100 calcium-binding protein A1 (S100A1) located in very distal part of TRPM4 N-terminus. (TRPM4 = transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 4) PMID: 29240297
- Data found that S100A1 was upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues, and its upregulation was associated with large tumor size, low differentiation, and shorter survival rates. Further results supports the hypothesis that S100A1 functions as an oncogene and may be a biomarker for the prognosis of patients with HCC. S100A1 exerted its oncogenic function by interacting with LATS1 and activating Hippo pathway. PMID: 29901195
- The results indicate that changes in the circulating level of S100A1 protein occur in metabolic syndrome patients. The strong correlation between serum zinc-alpha2-glycoprotein and S100A1 might suggest that production or release of these two proteins could be related mechanistically. PMID: 28825380
- The results indicated that S100A1 enhanced the ovarian cancer cell proliferation and migration. PMID: 28595036
- found that S100B plays a crucial role in blocking the interaction site between RAGE V domain and S100A1. A cell proliferation assay WST-1 also supported our results. This report could potentially be useful for new protein development for cancer treatment PMID: 29444082
- Study provides evidence that mir-363 and its target S100A1 are under the regulatory function of FOXD2-AS1 aggravating nasopharyngeal carcinoma carcinogenesis. PMID: 29248577
- X-ray crystal structure of human calcium-bound S100A1 has been reported. PMID: 28368280
- a molecular mechanism for the potential regulation of TRPM1 by S100A1 PMID: 27435061
- Data suggest that calcium signaling plays important role in prevention of protein misfolding; complexes of S100A1 and STIP1 are key players in this pathway; the stoichiometry of S100A1/STIP1 interaction appears to be three S100A1 dimers plus one STIP1 monomer; each S100A1-STIP1-binding interaction is entropically driven. (S100A1 = S100 calcium binding protein A1; STIP1 = stress-induced-phosphoprotein 1) [REVIEW] PMID: 28819010
- Data suggest that three dimers of S100A1 (S100 calcium binding protein A1) associate with one molecule of STIP1 (stress-inducible phosphoprotein 1) in a calcium-dependent manner; individual STIP1 TPR (tetratricopeptide repeat) domains, TPR1, TPR2A and TPR2B, bind a single S100A1 dimer with significantly different affinities; TPR2B domain possesses highest affinity for S100A1. PMID: 28408431
- Results identified amino acids motif in S100A1 for protein binding to 2-oxohistidine which appears to be an evolutionarily conserved capacity from bacteria to human. PMID: 27644758
- a correlation between S100B + A1-positive Human Articular Chondrocytes in monolayer culture and their neochondrogenesis capacity in pellet culture, is reported. PMID: 27861869
- In line with these observations, rhesus monkey rhadinovirus infection resulted in rapid degradation of SP100, followed by degradation of PML and the loss of ND10 structures, whereas the protein levels of ATRX and DAXX remained constant. PMID: 27356898
- High Serum protein S100 levels are associated with postoperative delirium after off-pump coronary artery bypass surgery. PMID: 26943607
- molecular dynamics simulations of S100A1 in the apo/holo (Ca(2+)-free/bound) states, is reported. PMID: 26958883
- The relationship between the degree of infiltration by S100-positive (S100+) dendritic cells and prognostic factors, including histological subtype, histological grade, peritumor inflammatory infiltration, and stromal desmoplasia, were examined. PMID: 25611268
- In this review, we aim to describe the molecular basis and regulatory function of S100A1--{REVIEW} PMID: 25157660
- Patients with acute myocardial infarction (MI) showed significantly increased S100A1 serum levels. S100A1 signaling in cardiac fibroblasts occurs through endosomal TLR4/MyD88. PMID: 24833748
- hypoxia-induced MiR-138 is an essential mediator of EC dysfunction via its ability to target the 3'UTR of S100A1. PMID: 24244340
- It was suggested that S100A1 and S100B be used as markers to develop potency assays for cartilage regeneration cell therapies, and as a redifferentiation readout in monolayer cultures aiming to investigate stimuli for chondrogenic induction. PMID: 24402969
- Twenty-seven out of thirty-two (84.38%) cases of serous ovarian carcinoma were found to express S100A1. S100A1 expression was observed in one out of the two mucinous and three out of the six endometroid ovarian carcinomas. PMID: 24501865
- The triple mutation Arg852/Lys859/Arg860 exhibited significant disruption of the binding of S100A1 to TRPC6 implicating their involvement in the binding site. PMID: 23671622
- For autopsy material, all human cases of definite myocardial infarction and suspected early infarction showed well-defined areas without S100A1 staining. PMID: 23683996
- This study showed that overexpression of S100A10, may play a role in irritable bowel syndrome, and that the IL10-819 CC is a candidate genotype for irritable bowel syndrome and ulcerative colitis. PMID: 23595519
- In this review we will focus on the roles of S100A proteins in intracellular and extracellular calcium signalling and homeostasis. PMID: 23662436
- the increased calcium binding affinity of S100A1 upon thionylation arises, most probably, from rearrangement of the hydrophobic core in its apo form PMID: 23351007
- Report downregulation of S100A1 expression in critical limb ischemia impairs postischemic angiogenesis via compromised proangiogenic endothelial cell function and nitric oxide synthase regulation. PMID: 23048072
- S-Nitrosylation of S100A1 increases Ca(2+) binding and tunes the overall protein conformation. PMID: 22989881
- Uremia clearance using NHD is accompanied by improvement in LV strain, rotation, reduction in mass and volume index. Dialysis downregulates genes for cardiomyocyte apoptosis and fibrosis and upregulates S100A1, which may improve LV contractility. PMID: 22647434
- Calmodulin and S100A1 protein interact with N terminus of TRPM3 channel. PMID: 22451665
- The three-dimensional structure of human apo(calcium free)S100A1 protein was determined by NMR spectroscopy PMID: 21296671
- Thermodynamics of zinc binding to human S100A2 PMID: 21090249
- S100A1, S100A2, S100A4, S100A6 and S100B interacted with MDM2 (2-125). PMID: 20591429
- A single phenyl-Sepharose column was sufficient for the purification of human S100A11 whereas HiTrap Q anion exchange followed by phenyl-Sepharose columns were required for the purification of S100A1. PMID: 20347987
- The expression of S100A1 was low in benign melanocytic tumours and increased in malignant melanomas PMID: 20042890
- S100A1B and S100BB are increased in urine collected from asphyxiated newborns who will develop hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) since first urination, and their measurement may be useful to early predict HIE. PMID: 19482672
- S100A1 is a specific and sensitive immunohistochemical marker to differentiate nephrogenic adenoma from prostatic adenocarcinoma PMID: 19384190
- The presence of the S100A1 in myocardial sarcoplasmic reticulum and myofibrils may be related to the known target proteins for S100A1 at these sites. PMID: 11829317
- Impaired cardiac contractility response to hemodynamic stress in S100A1-deficient mice. PMID: 11909974
- identification of the S100A1 C terminus (amino acids 75-94) and hinge region (amino acids 42-54) to differentially enhance sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release with a nearly 3-fold higher activity of the C terminus PMID: 12721284
- S100A1 has a reglatory role in the contraction-relaxation cycle in the human heart PMID: 12804600
- S100A1 protein serves as a cardioprotective factor in vitro PMID: 12960148
- identified S100A1, but not calmodulin or other S100 proteins, as a potent molecular chaperone and a new member of the Hsp70/Hsp90 multichaperone complex PMID: 14638689
- Synapsins and S100A1 interact in nerve terminals where coexpresssed; S100A1 cannot bind SV-associated synapsin I and may function as a cytoplasmic store of monomeric synapsin I; synapsin dimerization and interaction with S100A1 are mutually exclusive PMID: 15147519
- Results demonstrate that restoration of S100A1 protein levels in failing myocardium by gene transfer may be a novel therapeutic strategy for the treatment of heart failure. PMID: 15578088
- This study provides the first evidence that intracellular S100A1, depending on its subcellular location, modulates cardiac Ca2+-turnover via different Ca2+-regulatory proteins. PMID: 15654019
- S100A1 was expressed in 2/15 clear cell RCCs, 11/15 papillary RCCs, 7/8 oncocytomas and in 0/7 chromophobe RCCs. PMID: 15780567
- the three-dimensional structure of calcium-bound S100A1 was determined by multidimensional NMR spectroscopy and compared to the previously determined structure of apo-S100A1 PMID: 16169012
- S-100 protein expression in tumour cells was associated with significantly decreased survival PMID: 16760135
- analysis of the different reactivity pattern of S100A1 in the external auditory canal cholesteatoma PMID: 16969478
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Cytoplasm. Sarcoplasmic reticulum. Mitochondrion.
-
蛋白家族:S-100 family
-
組織特異性:Highly prevalent in heart. Also found in lesser quantities in skeletal muscle and brain.
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Rat Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CD44 antigen (CD44), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
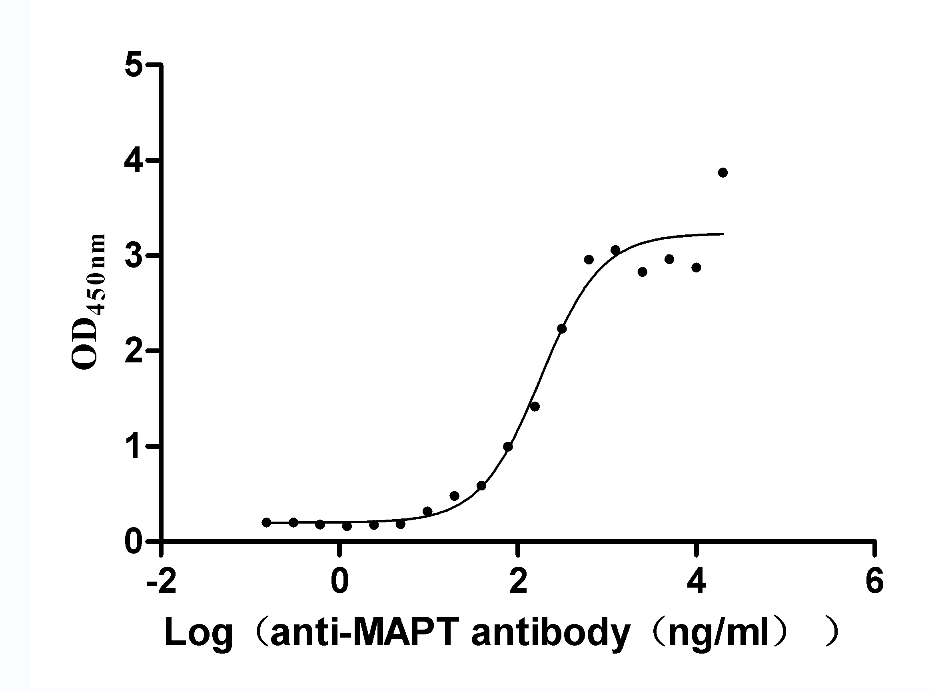
Recombinant Human Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
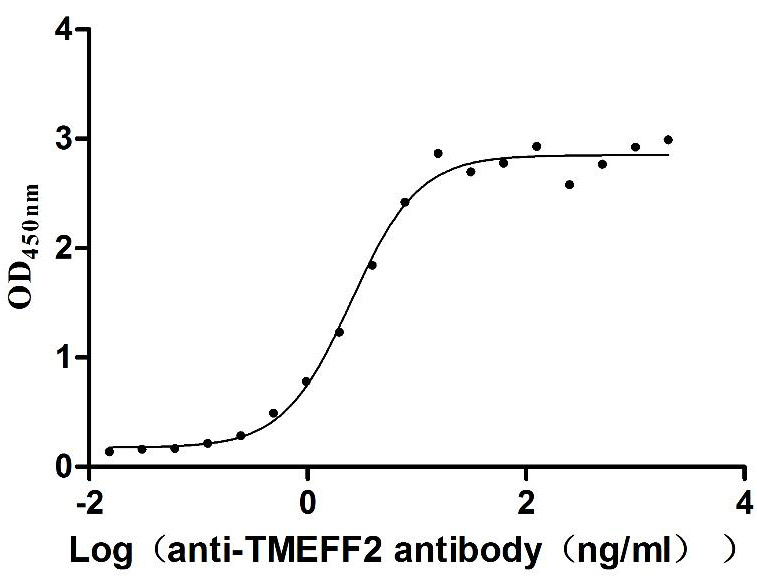
Recombinant Human Tomoregulin-2 (TMEFF2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
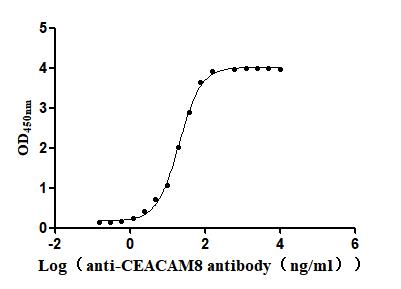
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8(CEACAM8) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
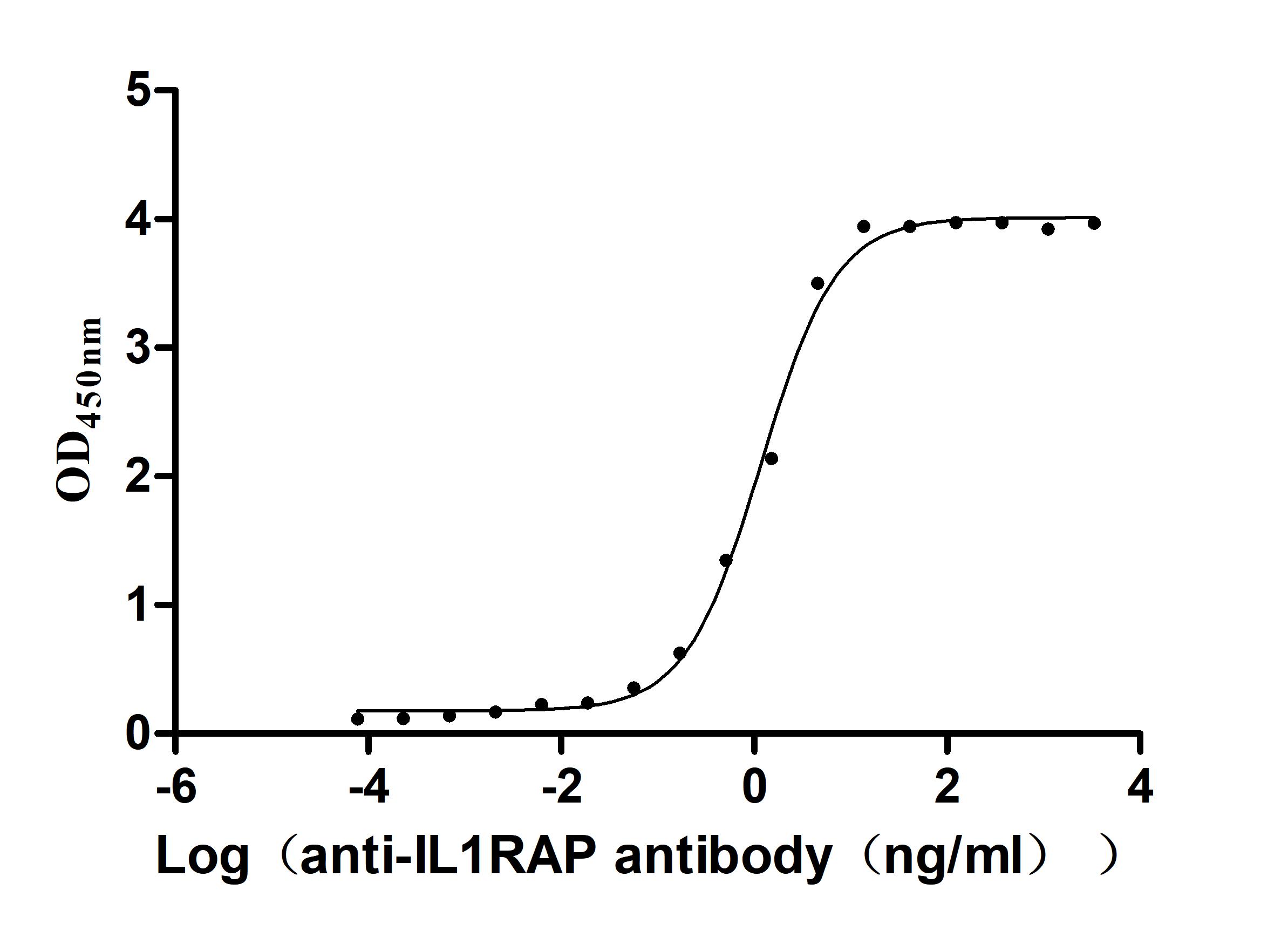
Recombinant Human Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAP), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)