Recombinant Human B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA), partial (Active)
In Stock-
中文名稱:
-
貨號:CSB-MP773799HU
-
規(guī)格:¥1368
-
圖片:
-
(Tris-Glycine gel) Discontinuous SDS-PAGE (reduced) with 5% enrichment gel and 15% separation gel.
-
Activity
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized BTLA at 5 μg/ml can bind biotinylated human TNFRSF14 (CSB-MP842173HU-A), the EC50 is 137.8-233.4 ng/ml. Biological Activity Assay
-
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
純度:Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
內(nèi)毒素:Less than 1.0 EU/ug as determined by LAL method.
-
生物活性:①Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized BTLA at 5 μg/ml can bind biotinylated human TNFRSF14 (CSB-MP842173HU-A), the EC50 is 137.8-233.4 ng/ml.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:(B- and T-lymphocyte-associated protein)(CD272)
-
分子結(jié)構(gòu):
-
種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白長度:Partial
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
分子量:43.9 kDa
-
表達區(qū)域:31-150aa
-
氨基酸序列KESCDVQLYIKRQSEHSILAGDPFELECPVKYCANRPHVTWCKLNGTTCVKLEDRQTSWKEEKNISFFILHFEPVLPNDNGSYRCSANFQSNLIESHSTTLYVTDVKSASERPSKDEMAS
-
蛋白標簽:C-terminal hFc-Myc-tagged
-
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
緩沖液:Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered PBS, 6% Trehalose, pH 7.4
-
復溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20°C/-80°C. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:3-7 business days
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
產(chǎn)品描述:
The recombinant human B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) was produced in mammalian cells. The DNA fragment used to prepare the recombinant BTLA protein corresponds to amino acid 31-150 of the human BTLA protein containing a C-terminal hFc-Myc-tag. This BTLA protein is an active protein, whose bio-activity has been validated in a functional ELISA (bind to biotinylated human TNFRSF14 with the EC50 of 137.8-233.4 ng/ml). Its purity reaches up to 94%, determined by SDS-PAGE. Due to the glycosylation, this BTLA protein has an apparent molecular mass of 55 kDa on the gel while its predicted mass is 43.9 kDa. Its endotoxin is less than 1.0 EU/ug measured by the LAL method. It is available now.
BTLA is an immunomodulatory molecule widely expressed on the surface of immune cells. Upon binding to its ligand HVEM, BTLA can influence various signaling pathways and negatively regulate the activation and proliferation of immune cells. It is implicated in the pathogenesis of many respiratory diseases, including airway inflammation, asthma, infection, and pneumonia.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Inhibitory receptor on lymphocytes that negatively regulates antigen receptor signaling via PTPN6/SHP-1 and PTPN11/SHP-2. May interact in cis (on the same cell) or in trans (on other cells) with TNFRSF14. In cis interactions, appears to play an immune regulatory role inhibiting in trans interactions in naive T cells to maintain a resting state. In trans interactions, can predominate during adaptive immune response to provide survival signals to effector T cells.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- Data suggest that both HVEM and UL144 bind a common epitope of BTLA, whether engaged in trans or in cis; these studies were conducted in cell lines representing B-lymphocytes, T-lymphocytes, and natural killer cells. (HVEM = human herpes virus entry mediator; UL144 = membrane glycoprotein UL144 of Human herpesvirus 5; BTLA = human B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator) PMID: 29061848
- our data suggested that the BTLA/HVEM pathway contributes to peripheral T cell suppression in hepatocellular carcinoma patients PMID: 30116751
- data provide the first evidence that increased BTLA predicts poor prognosis in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and blockade of BTLA with other checkpoints may potentially represent a new strategy for immunotherapy of DLBCL. PMID: 29353075
- The genetic variants of rs76844316 in BTLA influence the susceptibility to severe chronic hepatitis B and might play a protective role against the progression of chronic hepatitis B. PMID: 29558758
- The impairment of Bregs and CD19+/BTLA+ cells could play an important pathogenic role in multiple sclerosis (MS). PMID: 27412504
- Our data portrays BTLA as a molecule with the singular ability to provide both costimulatory and coinhibitory signals to activated CD8(+) T cells, resulting in extended survival, improved tumor control, and the development of a functional recall response. PMID: 28754817
- results indicate that polymorphisms rs1982809 situated in 3' UTR nearby region of BTLA gene might be considered as low-penetrating risk factor for RCC, but results have to be confirmed in further studies PMID: 27234378
- The percentage of circulating BTLA+CD4+ lymphocytes was significantly higher in patients with severe community acquired pneumonia. PMID: 28164546
- Plasma concentrations of soluble BTLA were increased early in sepsis/septic shock and correlated to severity of disease. A baseline concentration >21ng/mL was associated with a poor prognosis. PMID: 28056053
- this study shows that in chronic hepatitis B virus patients, a subset of inefficient interferon-gamma producing antigen-specific CD8+ T cells recruited to the liver expressed high BTLA levels PMID: 27743606
- this study shows that BTLA expression is likely associated with positive rather than conventional negative regulation of CD11c antigen-presenting cell stimulatory capacity PMID: 27717503
- rs1982809 BTLA gene polymorphism is associated with mRNA expression level and variations in the BTLA gene might be considered as potentially low-penetrating chronic lymphocytic leukemia risk factor PMID: 27933341
- Study showed a decreased expression of BTLA in ocular Behcet's disease suggesting that it may be involved in the development and recurrence of this disease. PMID: 26841832
- BTLA expression declines on B cells of the aged and is associated with low responsiveness to the trivalent influenza vaccine. PMID: 26277622
- our study confirms that CD200/BTLA deletions are recurrent genetic lesions in the biology of BCP-ALL PMID: 26137961
- Focal deletions of the BTLA were associated with B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. PMID: 25261097
- high BTLA expression levels in gastric cancer, identified by IHC, are an independent biomarker for the poor prognosis of patients with gastric cancer. PMID: 25334051
- Data indicate taht lung function and the expressions of B, T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) and Treg cells were lower in patients with rheumatism than those in normal controls. PMID: 24909289
- BTLA is a coreceptor that negatively regulates human Vgamma9Vdelta2 T-cell proliferation and has a role in immune escape for lymphoma cells PMID: 23692853
- BTLA and HVEM may have roles in graft rejection after kidney transplantation PMID: 23375291
- BTLA regulates human B cell responses and has implications for future development of therapies modulating B cells. PMID: 22903545
- The expression of BTLA has been observed on the surface of several kinds of cells within synovial tissues of RA patients, which indicates this signal might be involved in the regulation of local T cell activation and the pathogenesis of RA. PMID: 22691359
- These findings support role for BTLA and/or HVEM as potential, novel diagnostic markers of innate immune response/status and as therapeutic targets of sepsis. PMID: 22459947
- study described the expression and spatial distribution of HVEM and BTLA in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissues, and results indicated that HVEM/BTLA may be involved in regulating the progress of joint inflammation PMID: 22179929
- BTLA-HVEM interactions impair minor histocompatibiility antigen-specific T cell functionality, providing a rationale for BTLA signaling blockade in post-stem cell transplantation. PMID: 22634623
- Added with PD-1 and Tim-3 blockades, BTLA blockade enhanced the expansion, proliferation, and cytokine production of NY-ESO-1-specific CD8(+) T cells. PMID: 22205715
- HVEM-BTLA cis complex provides intrinsic regulation in T cells serving as an interference mechanism silencing signals coming from the microenvironment. PMID: 21920726
- The results of a mutagenesis study of HVEM suggest that the CD160 binding region on HVEM was slightly different from, but overlapped with, the BTLA binding site. PMID: 21959263
- 590C single-nucleotide polymorphism of B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator was significantly associated with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis, but not to systemic lupus erythematosus or Sjogren's syndrome. PMID: 21403914
- BTLA expression on overall CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells was progressively decreased in HIV-1 infection, which was directly correlated with disease progression and CD4(+) T-cell differentiation and activation PMID: 21592997
- In vitro blockade of the BTLA pathway augments allogeneic as well as cytomegalovirus-specific CD8-positive T cell proliferation, thereby enhancing the functional capacity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes in viral infections. PMID: 20693422
- BTLA gene polymorphisms may affect the sporadic breast cancer risk and prognosis in Chinese women in northeast of Heilongjiang Province PMID: 19585237
- Binding of HVEM to BTLA attenuates T cell activation, identifying HVEM/BTLA as a coinhibitory receptor pair. PMID: 15647361
- distinct herpesviruses target the HVEM-BTLA cosignaling pathway, suggesting the importance of this pathway in regulating T cell activation during host defenses. PMID: 16131544
- 2.8-A crystal structure of the BTLA-HVEM complex shows that BTLA binds the N-terminal cysteine-rich domain of HVEM and employs a unique binding surface PMID: 16169851
- BTLA is constitutively expressed on most CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and its expression progressively decreases upon T cell activation. PMID: 16643847
- Cross-linking of BTLA with mAb 7D7 suppressed T lymphocyte proliferation, downregulated the expression of T cell activation marker CD25, and inhibited the production of interferon (IFN)-gamma, interleukin (IL)-2, IL-4, and IL-10. PMID: 17257317
- BTLA is an inhibitory coreceptor of the B cell receptor (BCR) signaling pathway that attenuates B cell activation by targeting the downstream signaling molecules Syk and B cell linker protein (BLNK). PMID: 19155498
- this study did not find any genetic contribution of the BTLA gene to the development of T1D and SLE in Japanese population. PMID: 19207938
- results suggest that down-regulation of the BTLA-HVEM pathway may be involved in germinal center B-cell activation. PMID: 19762537
- the HVEM-BTLA cis-complex competitively inhibits HVEM activation by ligands expressed in the surrounding microenvironment, thus helping maintain T cells in the naive state. PMID: 19915044
- HVEM binds to B T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA), an Ig family member, which inhibits T cell proliferation. PMID: 15568026
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Pro-neuregulin-1, membrane-bound isoform (NRG1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
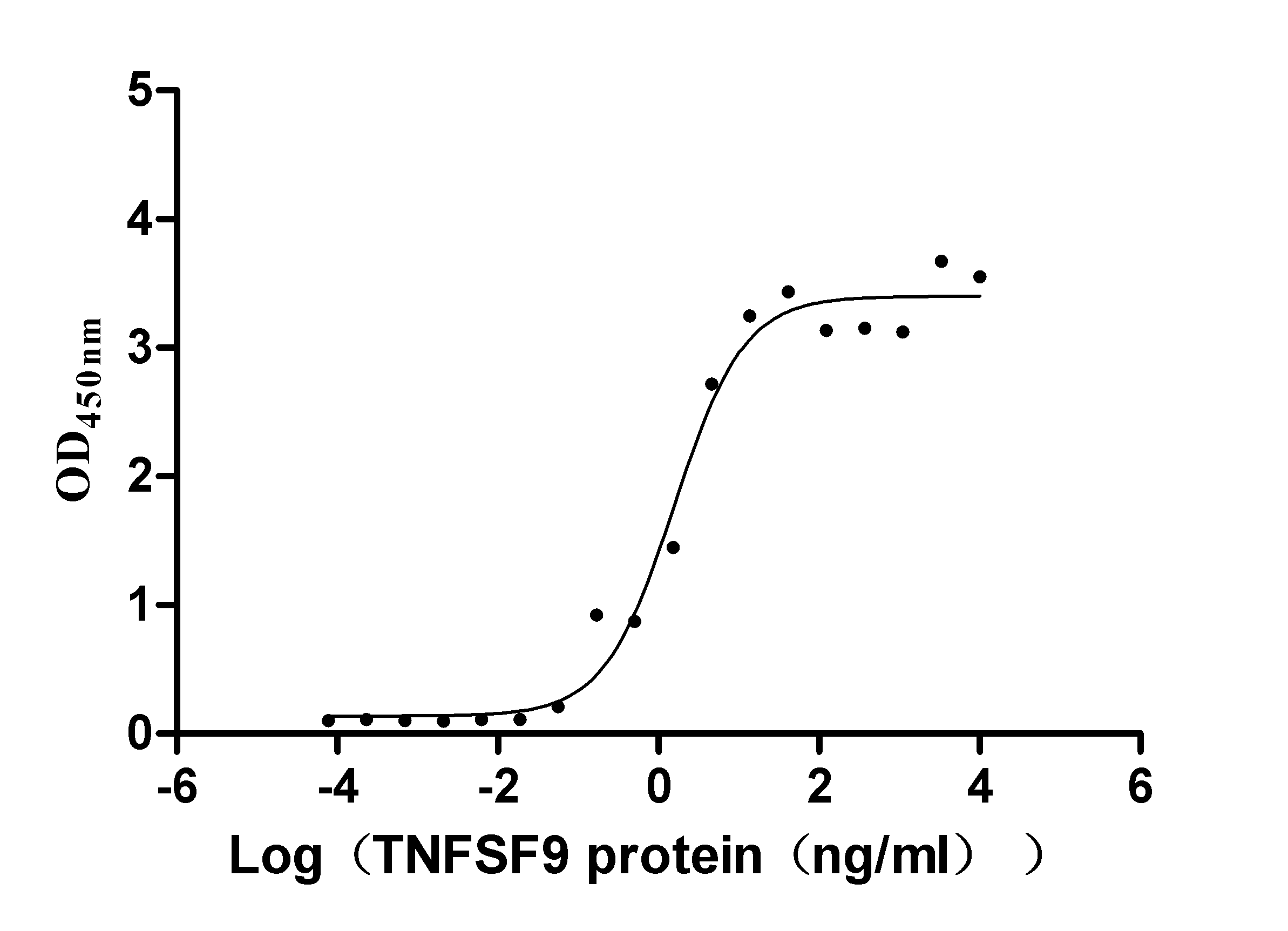
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 9 (TNFRSF9), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
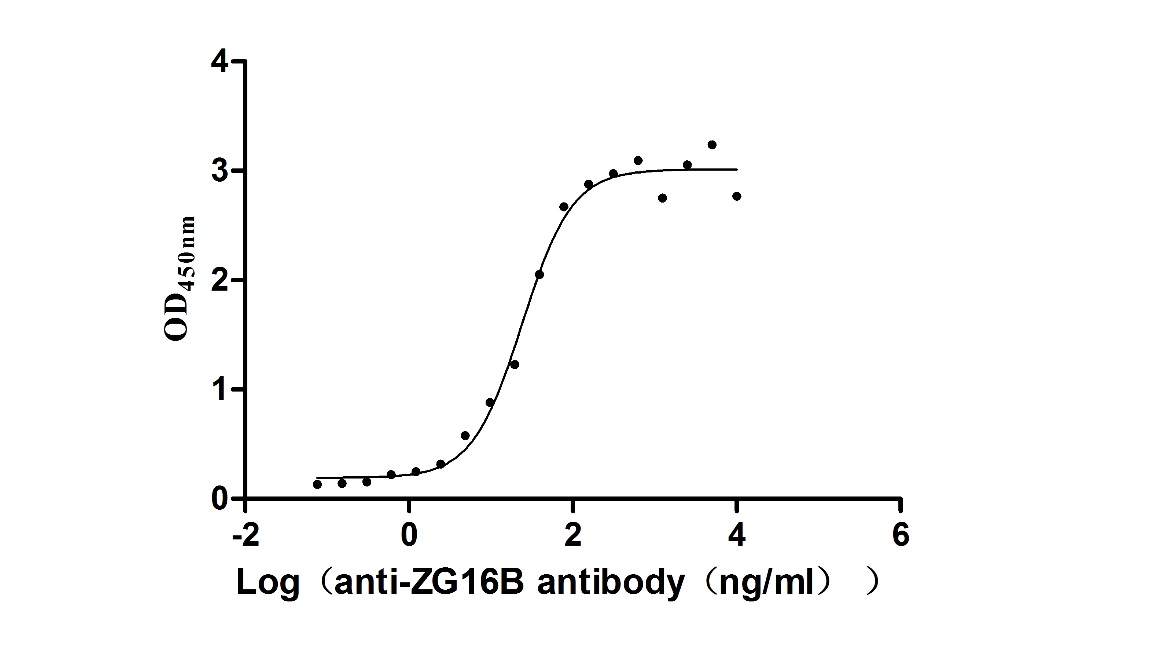
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
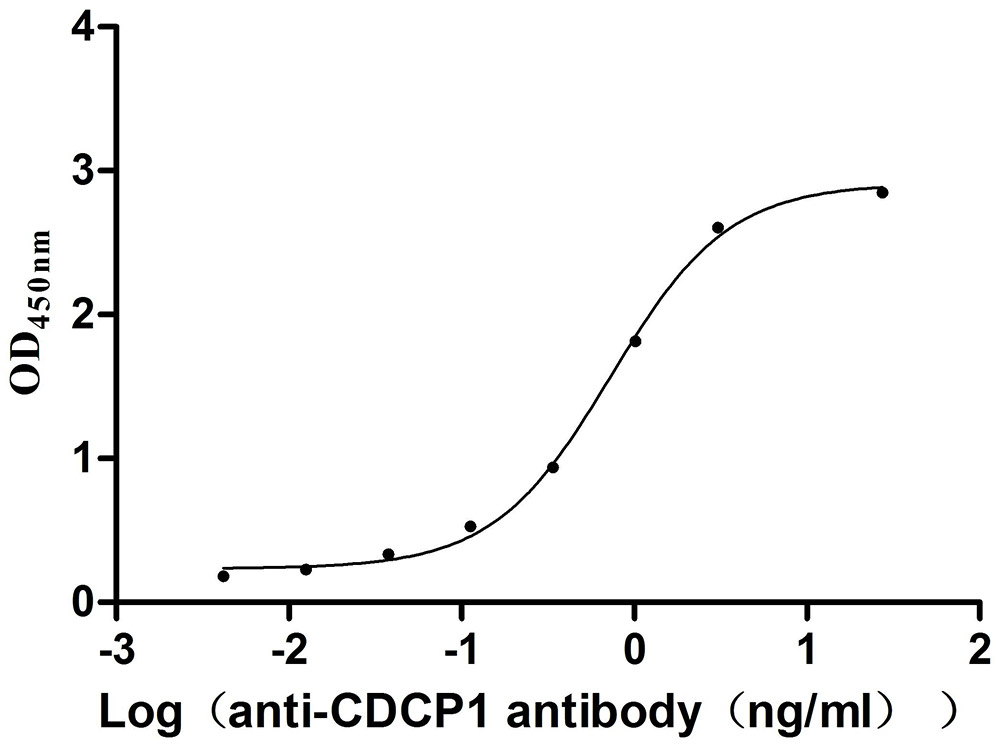
Recombinant Mouse CUB domain-containing protein 1 (Cdcp1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
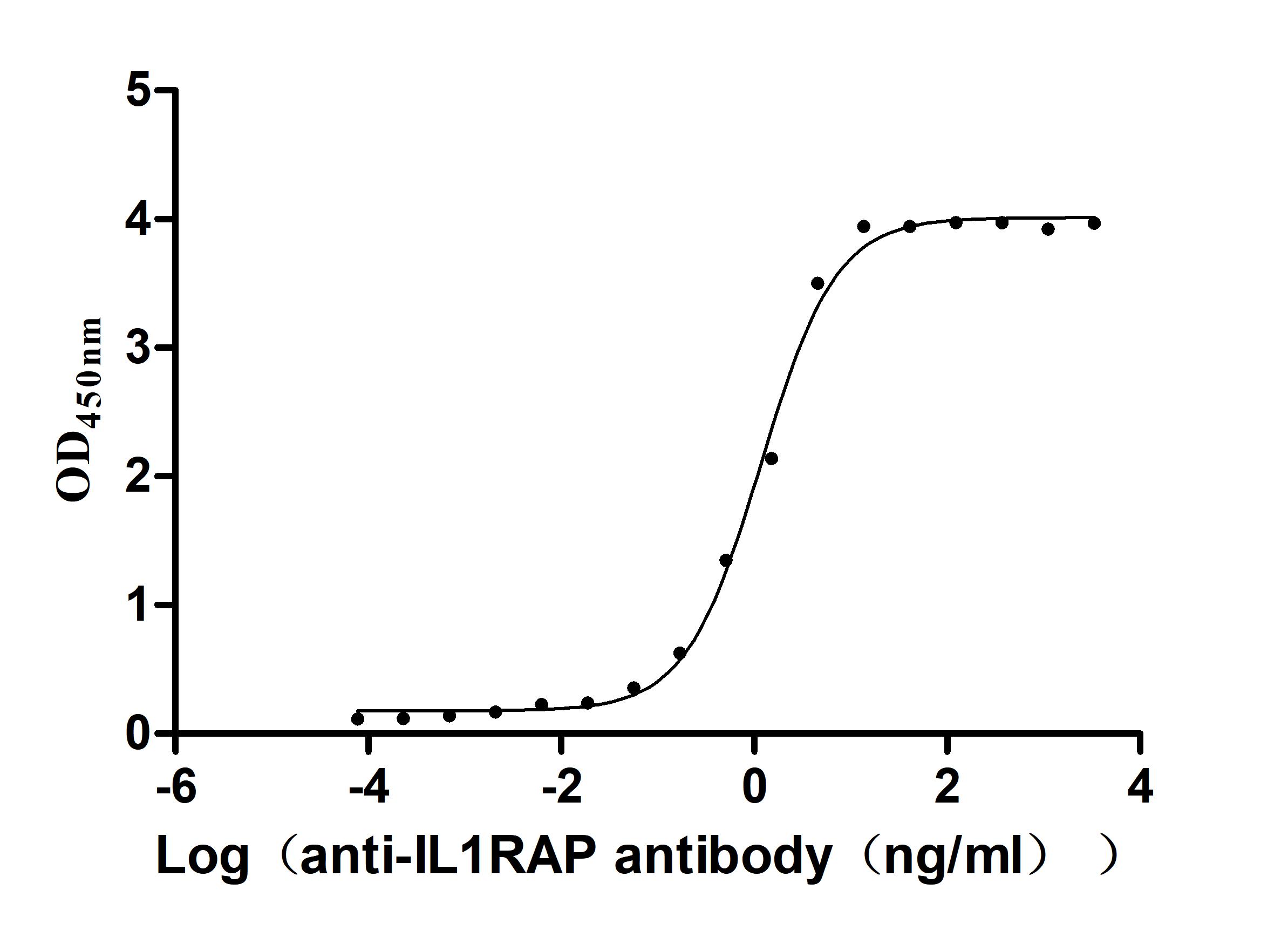
Recombinant Human Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAP), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)





-AC1.jpg)