Recombinant Human 85 kDa calcium-independent phospholipase A2 (PLA2G6), partial
-
中文名稱:人PLA2G6重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-YP018104HU
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:人PLA2G6重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP018104HU
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:人PLA2G6重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP018104HU-B
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:人PLA2G6重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-BP018104HU
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:人PLA2G6重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-MP018104HU
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:85 kDa calcium independent phospholipase A2; 85/88 kDa calcium-independent phospholipase A2; BB112799; CaI PLA2; CaI-PLA2; CaIPLA2; Calcium independent phospholipase A2; CTA-228A.2; Cytosolic calcium independent phospholipase A2; EC 3.1.1.4; Group VI phospholipase A2; Group VI, A; GVI; GVI PLA2; INAD1; Intracellular membrane associated calcium independent phospholipase A2 beta; Intracellular membrane-associated calcium-independent phospholipase A2 beta; iPLA(2)beta; iPLA2 beta; iPLA2-beta; IPLA2-VIA; iPLA2beta; NBIA2; NBIA2A; NBIA2B; Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation 2; OTTHUMP00000199457; PARK14; Patatin like phospholipase domain containing 9; Patatin like phospholipase domain containing protein 9; Patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 9; Phospholipase A2 calcium independent; Phospholipase A2 calcium independent group VI A; Phospholipase A2 group VI; Phospholipase A2 group VI cytosolic calcium independent; Phospholipase A2, group VI (cytosolic, calcium independent); PLA2; PLA2G6; PLPL9_HUMAN; PNPLA9
-
種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白長度:Partial
-
蛋白標(biāo)簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復(fù)溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項(xiàng):Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:Calcium-independent phospholipase involved in phospholipid remodeling with implications in cellular membrane homeostasis, mitochondrial integrity and signal transduction. Hydrolyzes the ester bond of the fatty acyl group attached at sn-1 or sn-2 position of phospholipids (phospholipase A1 and A2 activity respectively), producing lysophospholipids that are used in deacylation-reacylation cycles. Hydrolyzes both saturated and unsaturated long fatty acyl chains in various glycerophospholipid classes such as phosphatidylcholines, phosphatidylethanolamines and phosphatidates, with a preference for hydrolysis at sn-2 position. Can further hydrolyze lysophospholipids carrying saturated fatty acyl chains (lysophospholipase activity). Upon oxidative stress, contributes to remodeling of mitochondrial phospholipids in pancreatic beta cells, in a repair mechanism to reduce oxidized lipid content. Preferentially hydrolyzes oxidized polyunsaturated fatty acyl chains from cardiolipins, yielding monolysocardiolipins that can be reacylated with unoxidized fatty acyls to regenerate native cardiolipin species. Hydrolyzes oxidized glycerophosphoethanolamines present in pancreatic islets, releasing oxidized polyunsaturated fatty acids such as hydroxyeicosatetraenoates (HETEs). Has thioesterase activity toward fatty-acyl CoA releasing CoA-SH known to facilitate fatty acid transport and beta-oxidation in mitochondria particularly in skeletal muscle. Plays a role in regulation of membrane dynamics and homeostasis. Selectively hydrolyzes sn-2 arachidonoyl group in plasmalogen phospholipids, structural components of lipid rafts and myelin. Regulates F-actin polymerization at the pseudopods, which is required for both speed and directionality of MCP1/CCL2-induced monocyte chemotaxis. Targets membrane phospholipids to produce potent lipid signaling messengers. Generates lysophosphatidate (LPA, 1-acyl-glycerol-3-phosphate), which acts via G-protein receptors in various cell types. Has phospholipase A2 activity toward platelet-activating factor (PAF, 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine), likely playing a role in inactivation of this potent proinflammatory signaling lipid. In response to glucose, amplifies calcium influx in pancreatic beta cells to promote INS secretion.; Lacks the catalytic domain and may act as a negative regulator of the catalytically active isoforms.; Lacks the catalytic domain and may act as a negative regulator of the catalytically active isoforms.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- This study showed that PANK2 genes account for disease of patients diagnosed with an Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation disorder. PMID: 29325618
- A lipidomics-based LC/MS assay was used to define the specificity of cPLA2, iPLA2, and sPLA2 toward a variety of phospholipids. A unique hydrophobic binding site for the cleaved fatty acid dominates each enzyme's specificity rather than its catalytic residues and polar headgroup binding site. PMID: 29342349
- This exome sequencing in a family and identified compound-heterozygous PLA2G6 mutations in 2 affected sisters. PMID: 27709683
- PLA2G6 gene mutations in 3 families, are reported. PMID: 28295203
- The catalytic domains of iPLA2beta form a tight dimer and surrounded by ankyrin repeat domains that adopt an outwardly flared orientation, poised to interact with membrane proteins. PMID: 29472584
- performed a longitudinal brain volumetry study in a couple of bicorial twins with PLA2G6-positive infantile neuronal axonal dystrophy PMID: 28091863
- We found no significant influence of the PLA2G6 and PLA2G4C polymorphisms on mean age at first hospital admission (P > 0.05) and that the investigated polymorphisms significantly influenced the clinical psychopathology only in male patients. The PLA2G4C polymorphism accounted for approximately 12% of negative symptom severity. PMID: 28651698
- Study performed direct sequencing and investigated copy number variations (CNVs) of this gene in 109 Japanese patients with parkinsonism. Results suggest that CNV in PLA2G6 is rare in parkinsonism, at least in the Japanese population, in contrast to the reports of its frequency in neurodegeneration associated with brain iron accumulation. PMID: 27942883
- the association of PLA2G6 with the pathogenesis of idiopathic PD, in addition to PARK14. PMID: 28213071
- A novel missense mutation in PLA2G6 gene (c.3G > T:p.M1I) in one and half-year-old boy with muscle weakness and neurodevelopmental regression (speech, motor and cognition). PMID: 28821231
- PLA2G6 were identified in patients with a spectrum of neurodegenerative conditions, such as infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy, atypical late-onset neuroaxonal dystrophy and dystonia parkinsonism complex in Indian families PMID: 27196560
- This study identifies a novel PLA2G6 mutation that is the possible genetic cause of FCMTE in this Chinese family. PMID: 27513994
- Finding suggest the broadness of the clinical spectrum of group VI phospholipases A2 (PLA2G6)-related neurodegeneration. PMID: 27268037
- A homozygous novel mutation at position c.2277-1G>C in PLA2G6 gene presumed to give rise to altered splicing, was detected, thus confirming the diagnosis of infantile Neuroaxonal Dystrophy (INAD). PMID: 25348461
- Three catalytically active cPLA2, iPLA2, and sPLA2 are expressed in different areas within the human spermatozoon cell body. Spermatozoa with a significant low motility showed strong differences both in terms of total specific activity and of different intracellular distribution, compared with normal spermatozoa. Phospholipases could be potential biomarkers of asthenozoospermia. PMID: 26446356
- This study demonstrated that elevated expression of alphaSyn/PalphaSyn in mitochondria appears to be the early response to PLA2G6-deficiency in neurons. PMID: 27030050
- Stimulation of adrenoreceptors causes increased iPLA2 expression via MAP kinase/ERK 1/2. PMID: 25482049
- genetic association study in Quebec City population: Data suggest total plasma n-6 fatty acid phospholipid levels and C-reactive protein are modulated by SNPs in PLA2G4A and PLA2G6 alone or in combination with fish oil dietary supplementation. PMID: 26525102
- Mutations in PLA2G6 altered Golgi morphology, O-linked glycosylation and sialylation of protein in patients with neurodegeneration PMID: 26668131
- PLA2G6 mutations in Indian patients with infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy and atypical late-onset neuroaxonal dystrophy PMID: 27196560
- Results demonstrated no significant impact of PLA2G6 and PLA2G4C gene polymorphisms on attenuated niacin skin flushing in schizophrenia patients. PMID: 26160611
- Analysis of the cells from idiopathic Parkinson's disease patients reveals a significant deficiency in store-operated PLA2g6-dependent Ca(2+) signalling PMID: 26755131
- Mutations in PANK2 and CoASY lead, respectively, to PKAN and CoPAN forms of Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation . Mutations in PLA2G6 lead to PLAN. Mutations in C19orf12 lead to MPAN PMID: 25668476
- our findings demonstrate that loss of normal PLA2G6 gene activity leads to lipid peroxidation, mitochondrial dysfunction and subsequent mitochondrial membrane abnormalities. PMID: 26001724
- genetic association studies in a population of Han Chinese: Data suggest that SNPs in PLA2G6 (rs132984; rs2284060) are associated with type 2 diabetes and hypertriglyceridemia in the population studied. [Meta-Analysis included] PMID: 25207958
- The loss of PS2 could have a critical role in lung tumor development through the upregulation of iPLA2 activity by reducing gamma-secretase. PMID: 24858037
- Novel PLA2G6 mutations were identified in all patients with Phospholipase A2 associated neurodegeneration. PMID: 24745848
- our findings indicate that PRDX6 promotes lung tumor growth via increased glutathione peroxidase and iPLA2 activities PMID: 24512906
- IL-1beta and IFNgamma induces mSREBP-1 and iPLA2beta expression and induce beta-cell apoptosis. PMID: 25004092
- The significance of calcium-independent phospholipase A, group VIA (iPLA2-VIA), in retinal pigment epithelial cell survival, was investigated. PMID: 24791136
- clinical findings may be helpful in distinguishing PLA2G6-related neurodegeneration from the other major cause of NBIA, recessive PANK2 mutations. PMID: 24522175
- the phenotype of neurodegeneration associated with PLA2G6 mutations PMID: 24130795
- This study demonistrated that PLA2g8 expression was significantly decreased in patients treated with antipsychotic drug. PMID: 23587695
- The association with bipolar disorder of the iPLA2beta (PLA2G6) its genetic interaction with type 2 transient receptor potential channel gene TRPM2, was examined. PMID: 23277130
- identified four rare PLA2G6 mutations in 250 PD patients in Chinese population with Parkinson's disease PMID: 23182313
- Mutations in PLA2G6 is often associated with rapidly progressive parkinsonism and with additional features including pyramidal signs, cognitive decline and loss of sustained Levodopa responsiveness. PMID: 23196729
- Neuronal phospholipid deacylation is essential for axonal and synaptic integrity through the action of iPLA2 and NTE. (Review) PMID: 22903185
- Orai1 and PLA2g6 are involved in adhesion formation, whereas STIM1 participates in both adhesion formation and disassembly. PMID: 23043102
- Findings reveal for the first time expression of iPLA(2)beta protein in human islet beta-cells and that induction of iPLA(2)beta during endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to human islet beta-cell apoptosis. PMID: 23074238
- membrane composition and the presence of nucleotides play key roles in recruiting and modulating GVIA-iPLA(2) activity in cells PMID: 23007400
- The present study confirms the involvement of iPLA(2)-VIA in efficient retinal pigment epithelium phagocytosis of photoreceptor outer segments. PMID: 22680611
- Different and even identical PLA2G6 mutations may cause neurodegenerative diseases with heterogeneous clinical manifestations, including dystonia-parkinsonism. PMID: 19087156
- The results of this study suggested that PLA2G6 is not a susceptibility gene for parkinson disease in our population. PMID: 22459563
- Our result indicated that PLA2G6 mutations might not be a main cause of Chinese sporadic early-onset parkinsonism. PMID: 22406380
- These data confirm the role of iPLA(2)beta as an essential mediator of endogenous store operated calcium entry. PMID: 22549787
- This report further defines the clinical features and neuropathology of PLA2G6 related childhood and adult onset dystonia-parkinsonism . PMID: 20619503
- PLA2G6 mutations are associated with PARK14-linked young-onset parkinsonism and sporadic Parkinson's disease PMID: 22213678
- acts as an inhibitory modulator of NKCC2 activity in thick ascending limb PMID: 22218592
- A possible involvement of calcium-independent group VI phospholipase A2 (iPLA2-VI) in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease has been proposed. PMID: 21812034
- data indicate that PLA2G6 mutation may not play a major role in general frontotemporal type of dementia PMID: 21482170
顯示更多
收起更多
-
相關(guān)疾病:Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation 2B (NBIA2B); Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation 2A (NBIA2A); Parkinson disease 14 (PARK14)
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Cytoplasm. Cell membrane. Mitochondrion. Cell projection, pseudopodium.
-
組織特異性:Four different transcripts were found to be expressed in a distinct tissue distribution.
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 14 (TNFRSF14), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
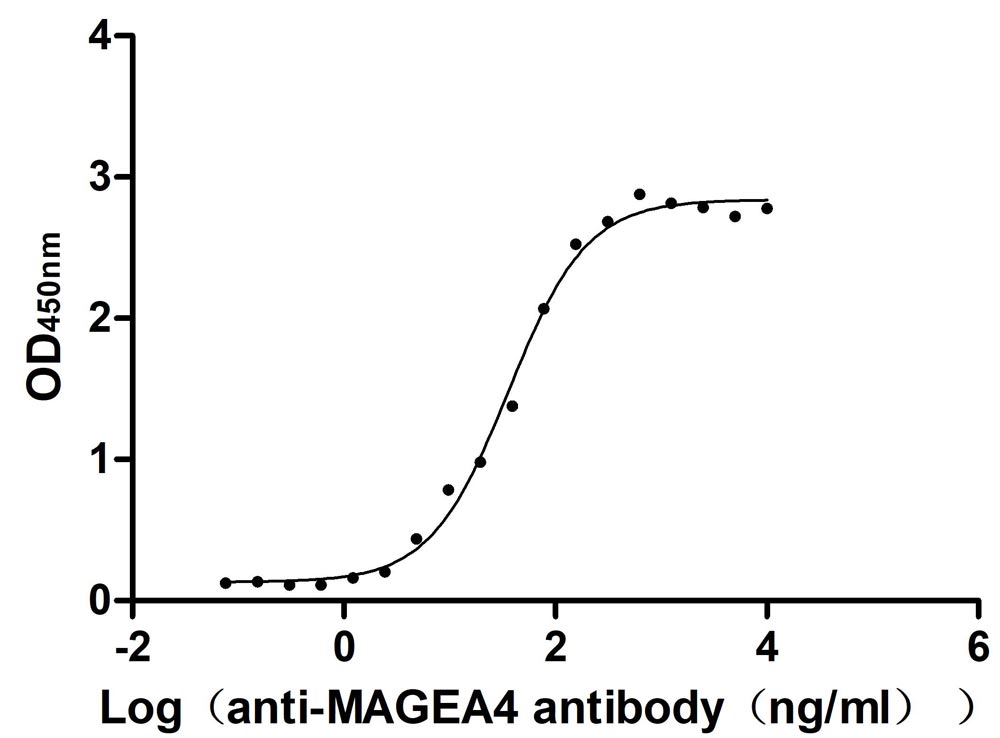
Recombinant Human Melanoma-associated antigen 4 (MAGEA4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Rat Intestinal-type alkaline phosphatase 1 (Alpi) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
Recombinant Human Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus protein G6d (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-2 (DSG2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light chain 12A (MYL12A) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
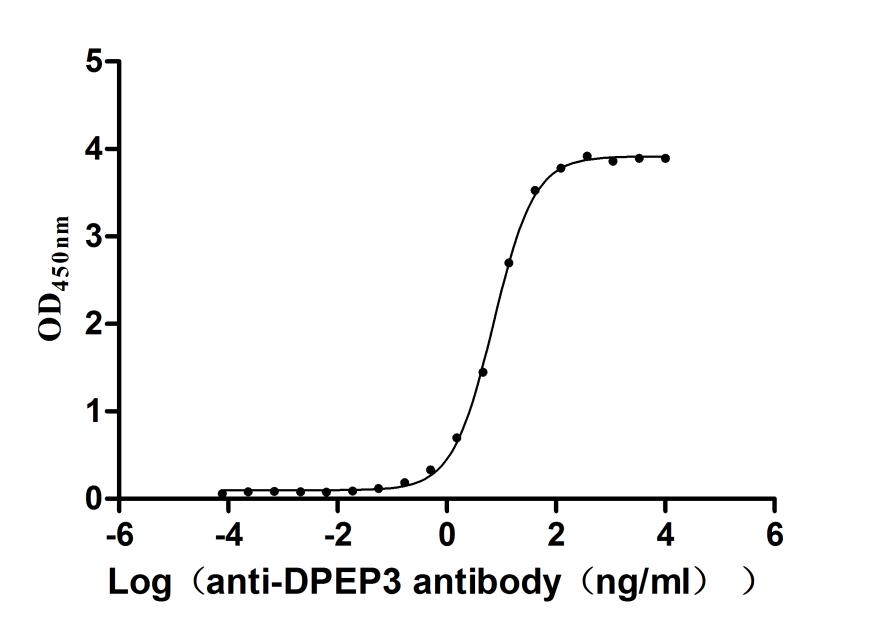
Recombinant Human Dipeptidase 3(DPEP3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
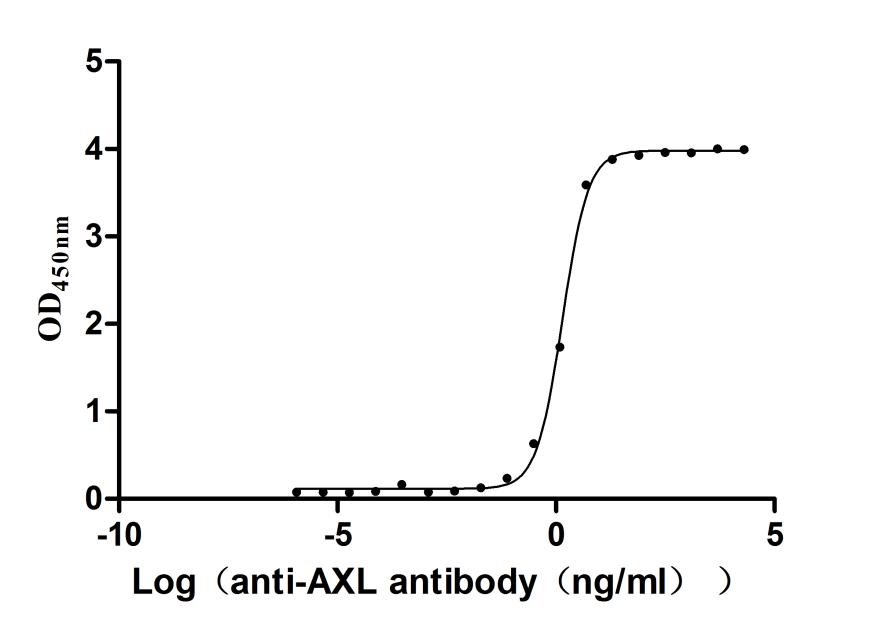
Recombinant Human Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor UFO(AXL),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)