VIPR1 Antibody
-
中文名稱:VIPR1兔多克隆抗體
-
貨號(hào):CSB-PA006153
-
規(guī)格:¥880
-
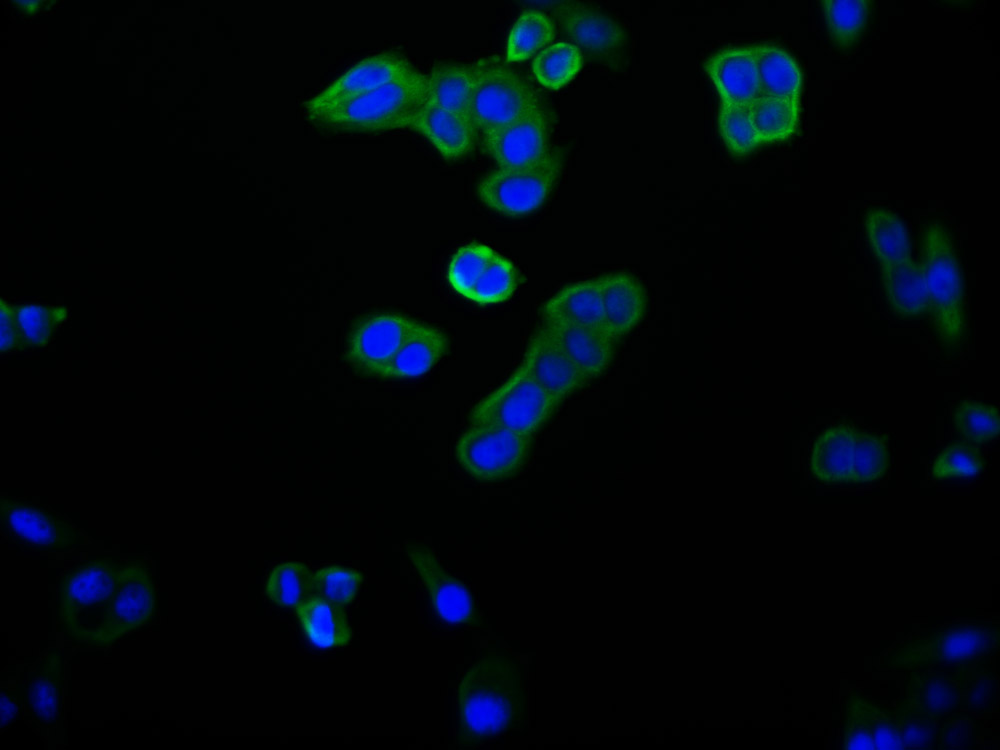
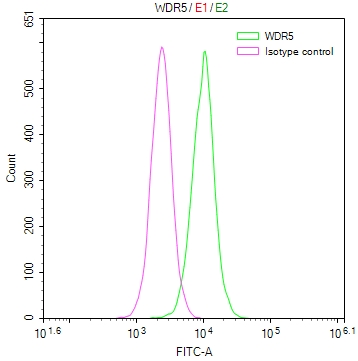
圖片:
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:
-
別名:VIPR1; Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide receptor 1; VIP-R-1; Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide type II receptor; PACAP type II receptor; PACAP-R-2; PACAP-R2; VPAC1
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應(yīng)種屬:Human
-
免疫原:Synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of Human VPAC1.
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
標(biāo)記方式:Non-conjugated
-
抗體亞型:IgG
-
純化方式:The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
-
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Liquid
-
應(yīng)用范圍:WB, ELISA
-
推薦稀釋比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:2000 ELISA 1:10000 -
Protocols:
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:This is a receptor for VIP. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylyl cyclase. The affinity is VIP = PACAP-27 > PACAP-38.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- In vitro-polarized macrophages by GM-CSF (GM-MO), with a proinflammatory profile, expressed higher levels of VIP receptors, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide receptors 1 and 2 (VPAC1 and VPAC2, respectively), than macrophages polarized by M-CSF (M-MO) with anti-inflammatory activities. RA synovial macrophages, according to their GM-CSF-like polarization state, expressed both VPAC1 and VPAC2. PMID: 27381006
- VPAC1 rs9677 CC genotype could be correlated with a reduced response to statin therapy and seems to be involved in diabetes cardiomyopathy in female patients with type 2 diabetes. PMID: 26712708
- The results reveal that more severe inflammation, based on high levels of IL-6, is associated with lower expression of VPAC1 and, conversely, with increased expression of VPAC2. PMID: 26881970
- variations at the 3'UTR of the VPAC-1 gene act synergistically to affect the expression of the luciferase as well as of the GFP reporter genes expressed in HEK293T cells. PMID: 25390694
- These data suggest that VPAC1 overexpression is associated with poorer differentiation of colon cancer, which is likely caused by subsequent EGFR activation in cancer cells. PMID: 24671823
- VPAC1 receptor has a role in endotoxemia in peripheral blood mononuclear cells PMID: 23651810
- The overexpression of VPAC1 and VPAC2 receptors and COX-2 in cancer tissue gives them a potential role as targets for diagnosis of prostate cancer. PMID: 22763881
- hree residues play an important role in VPAC1 interaction with the first histidine residue of VIP. These data demonstrate that VIP and PG97-269 bind to distinct domains of VPAC1 PMID: 22291440
- The genetic association reported here indicates that VIP/VPAC1 signaling can be a relevant pathway in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes in females PMID: 22166542
- silencing of VPAC1 receptor inhibits vasoactive intestinal peptide effects on both EGF receptor and HER2 transactivation and vascular endothelial growth factor secretion in human breast cancer cells PMID: 21896307
- mRNA expression of the VPAC1 receptor was detected in 51% of the tumor specimens, while the incidence of mRNA expression for VPAC2 was 46%. PMID: 21769421
- increased expression in patients with allergic rhinitis PMID: 21711977
- The VIPR1 polymorphism, previously linked to gastrointestinal dysmotility disorders, does not represent a common risk factor for gallstones in the general or in an elderly population. PMID: 20922191
- Moreover, we report the markedly nuclear localization of VPAC(1) receptors in estrogen-dependent (T47D) and independent (MDA-MB-468) human breast cancer cell lines PMID: 20691743
- role of in MicroRNA 525-5p down-modulating VPAC1 expressio PMID: 20706588
- Results indicate that VPAC1, but not VPAC2 or PAC1, up-regulation in macrophages is a common mechanism in response to acute and chronic pro-inflammatory stimuli. PMID: 20026142
- We describe significant upregulation of the SPP1 gene, downregulation of VIPR1, and losses of the VIPR1 gene. PMID: 20014941
- Vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor-1 (VPAC-1) is a novel gene target of the hemolymphopoietic transcription factor Ikaros. PMID: 11812772
- VPAC1 is a cellular neuroendocrine receptor expressed on T cells that actively facilitates productive HIV-1 infection. PMID: 11834941
- Thus, the highly diverged chemical properties of the hydrophobic "YL" motif and charged "DR(Y)" motif could be a crucial difference between the Secretin Receptor Family and the Rhodopsin Family with respect to receptor activation and G-protein coupling. PMID: 11859928
- VPAC1 receptor mRNA is expressed in the trigeminal, otic and superior cervical ganglia (prejunctional) and cerebral arteries (postjunctional). PMID: 11930171
- a small sequence in the third intracellular loop of the VPAC(1) receptor is responsible for the efficient agonist-stimulated intracellular calcium concentration increase PMID: 11981043
- Genetic complexity of HVR1 quasispecies of hepatitis C virus in patients with cirrhosis. PMID: 12094871
- a selective filter; Identification of a critical domain for restricting secretin binding PMID: 12133828
- the role of charged residues in the intracellular loop 3 and the proximal C-terminal tail of hVPAC1 receptor for agonist-induced adenylyl cyclase activation PMID: 12690118
- cloning and sequencing of 5' flanking region; VPAC1 may play a functional role in development of both cerebellum and adrenal medulla PMID: 14599709
- Data suggest that vasoactive intestinal peptide directly stimulates cortisol secretion from H295 cells via activation of the VPAC1 receptor subtype. PMID: 15171718
- the hVPAC1 receptor binds to vasoactive intestinal peptide at its N-terminal ectodomain PMID: 15247290
- Interaction of different G proteins with the recombinant VPAC1 receptor involves different receptor sub-domains. PMID: 15451021
- the VPAC1 receptor carboxyl terminus has a role in agonist-induced receptor phosphorylation, internalization, and recycling PMID: 15932876
- Farnesoid X receptor agonists may increase gallbladder fluid secretion through transcriptional activation of VPAC1. PMID: 16037943
- analysis of the two-step activation mechanism of VPAC receptor and of class II G protein-coupled receptors PMID: 16520374
- Thr429 phosphorylation has a role in activation of human VPAC1 PMID: 16554109
- 125I-[Bpa28-vasoactive intestinal peptide] was covalently bonded to the 121-133 fragment within the N-terminal ectodomain of the receptor PMID: 16888162
- Photoaffinity experiments clearly indicated that the 6-28 part of VIP physically interacts with the N-terminal ectodomain of VPAC1 receptor PMID: 16888167
- MCF-7 cells have VPAC1 receptors that bound the VIP chemotherapeutic conjugate PMID: 16888206
- observations provide additional evidence for a role of proapoptotic caspase adaptor protein and PAC1 R in the events determining the outcome of prostate cancer PMID: 16888207
- identification and characterization of novel five-transmembrane(5TM) isoforms of VPAC1 PMID: 16934434
- expression of VIP receptor-1 (VPAC1) and VPAC2 in CD4+ T cells changed reciprocally in the context of the activation state PMID: 17077178
- The differential expression of VIPR1 in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease mucosa suggests that the VIP system plays different roles in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. PMID: 17611633
- Both intra- and extracellular Ca2+ play a role in controlling pro-inflammatory functions stimulated by PACAP which acts through a VPAC-1, FPRL1/Galphai/PI3K/ERK pathway and a VPAC-1/Galphas/PKA/p38 pathway to fully activate monocytes PMID: 17651798
- analysis of VIP 16gamma-glutamyl diamino derivative positive charges on hVPAC1 and hVPAC2 receptor function PMID: 17883247
- VPAC1 signaling tempers normal megakaryopoiesis, and inhibition of this pathway stimulates megakaryocyte differentiation. PMID: 18000164
- Proinflammatory effect of VIP is mediated via the specific G protein-coupled receptor VIP/pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating protein (VPAC1) receptor as well as via FPRL1. PMID: 18174366
- deficient expression of VPAC1 (vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor 1) in immune cells of Rheumatoid Arthritis was associated with the predominant proinflammatory Th1 mileu; reduced VPAC1 expression in RA is associated with genetic polymorphism PMID: 18383379
- Results indicate that the N-terminal part of VIP physically interacts with the N-ted in the continuity of 6-28 VIP sequence; and the N-terminal part of VIP and its antagonist (PG97-269) have different sites of interaction with the VPAC1 receptor N-ted. PMID: 18597186
- HLA-B (*)2705 and a functional polymorphism in VIPR1 gene, might be due to a founder effect or might be the result of a selective pressure. Consequent downregulation of this receptor in presence of a 'danger' signal might influence susceptibility to AS. PMID: 18668120
- Patients with idiopathic achalasia show a significant difference in allele, genotype and phenotype of VIPR1 distribution of snps PMID: 19309439
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:G-protein coupled receptor 2 family
-
組織特異性:In lung, HT-29 colonic epithelial cells, Raji B-lymphoblasts. Lesser extent in brain, heart, kidney, liver and placenta. Not expressed in CD4+ or CD8+ T-cells. Expressed in the T-cell lines HARRIS, HuT 78, Jurkat and SUP-T1, but not in the T-cell lines Pe
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-