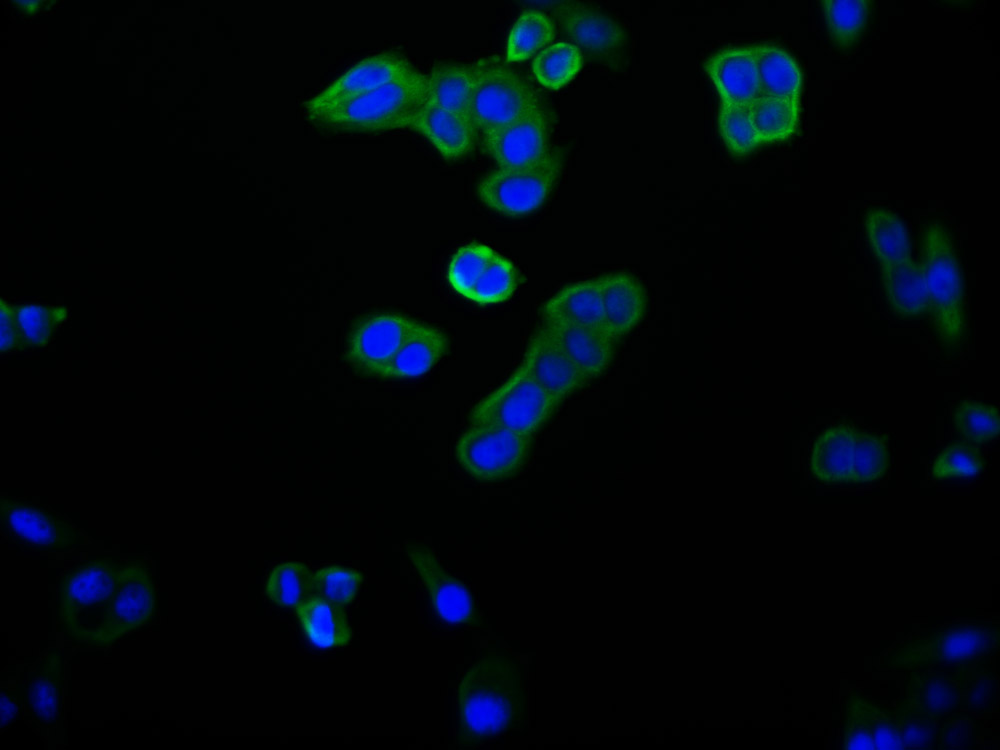
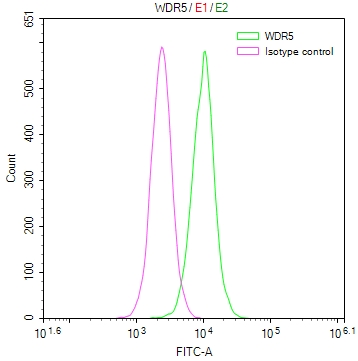
Phospho-SMC1A (S966) Antibody
-
中文名稱:磷酸化-SMC1A (S966)兔多克隆抗體
-
貨號:CSB-PA060230
-
規(guī)格:¥880
-
圖片:
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:
-
別名:Chromosome segregation protein SmcB antibody; DXS423E antibody; KIAA0178 antibody; MGC138332 antibody; Sb1.8 antibody; Segregation of mitotic chromosomes 1 antibody; SMC protein 1A antibody; SMC-1-alpha antibody; SMC-1A antibody; SMC1 (structural maintenance of chromosomes 1 yeast) like 1 antibody; SMC1 antibody; SMC1 structural maintenance of chromosomes 1 like 1 antibody; SMC1A antibody; SMC1A_HUMAN antibody; SMC1alpha antibody; SMC1L1 antibody; SMCB antibody; Structural maintenance of chromosomes 1A antibody; Structural maintenance of chromosomes protein 1A antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應(yīng)種屬:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Synthesized peptide derived from Human SMC1 around the phosphorylation site of S966.
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
標(biāo)記方式:Non-conjugated
-
抗體亞型:IgG
-
純化方式:The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
-
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Liquid
-
應(yīng)用范圍:WB, IHC, ELISA
-
推薦稀釋比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:2000 IHC 1:100-1:300 ELISA 1:10000 -
Protocols:
-
儲存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Involved in chromosome cohesion during cell cycle and in DNA repair. Central component of cohesin complex. The cohesin complex is required for the cohesion of sister chromatids after DNA replication. The cohesin complex apparently forms a large proteinaceous ring within which sister chromatids can be trapped. At anaphase, the complex is cleaved and dissociates from chromatin, allowing sister chromatids to segregate. The cohesin complex may also play a role in spindle pole assembly during mitosis. Involved in DNA repair via its interaction with BRCA1 and its related phosphorylation by ATM, or via its phosphorylation by ATR. Works as a downstream effector both in the ATM/NBS1 branch and in the ATR/MSH2 branch of S-phase checkpoint.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- Both the SMC1A and SMC3 gene mutation tests were negative in all Chinese patients with Cornelia de Lange syndrome. PMID: 29452578
- maintenance of the cancer cell state is dependent on recruitment of Mediator and Cohesin through FOXA and master transcription factors PMID: 27739523
- We conclude that SMC1A variants can result in a phenotype resembling CdLS and a phenotype resembling Rett syndrome. Resemblances between the SMC1A group and the NIPBL group suggest that a disturbed cohesin function contributes to the phenotype, but differences between these groups may also be explained by other underlying mechanisms such as moonlighting of the cohesin genes. PMID: 28548707
- All the nine probands with syndromic craniosynostosis were found to carry the possibly causative variants, among which three variants including two missense mutations in IFT122 gene, in SMC1A gene and a frameshift mutation in TWIST1 gene have never been reported in patients before. PMID: 29037998
- Based on these findings, LVNC cardiomyopathy and cleft lip should be considered features of SMC1A-associated CdLS. All patients should receive echocardiogram and undergo thorough ophthalmologic evaluation as part of routine CdLS care. PMID: 28102598
- Elevated expression of SMC1A in colorectal cancer cells promoted liver metastasis by recruiting the circulating tumor-associated fibroblasts. PMID: 27826041
- This study demonstrated that Truncation mutations in SMC1A cause a severe epilepsy phenotype with cluster seizures in females. PMID: 28166369
- Our data show the existence of a novel phenotypic entity - distinct from Cornelia de Lange syndrome - and caused by de novo SMC1A loss-of-function mutations PMID: 26752331
- We identified a large number of mutations in the CC region of both Smc1 and Smc3... we introduced them to the yeast Smc1 and Smc3 CC domains and characterized the effect of these mutant alleles on cohesin's function. We identified a missense mutation in the region of the kink domain of Smc3, which was previously identified in kidney carcinoma. PMID: 27307603
- High SMC1A expression is associated with prostate cancer. PMID: 27667360
- Results showed that the high expression of SMC1 often promoted epithelial-mesenchymal transition, accompanied by the enhanced expression of Brachyury in triple-negative breast cancer cells. PMID: 26781859
- SMC1A plays an oncogenic role in colorectal cancer. PMID: 26637483
- Loss-of-function mutations of SMC1A may be associated with early-onset encephalopathy with epilepsy. PMID: 26358754
- numerous dysregulated genes occupied by cohesin by combining the transcriptome of CdLS cell lines carrying mutations in SMC1A gene, were identified. PMID: 26581180
- two novel de novo heterozygous frameshift mutations in the SMC1A gene were identified in two patients with developmental delay and epilepsy. PMID: 26386245
- Our findings identify both SMC1 and CTCF as critical regulators of the differentiation-dependent life cycle of high-risk human papillomaviruses PMID: 25875106
- same down-regulation of cohesin targets is observed in SMC1A-mutated patient fibroblasts PMID: 26206533
- Results show that SMC1A is overexpressed in colorectal cancer tissues and correlated with poor prognosis for late stage disease. PMID: 25884313
- The SMC1a mutation leads to chromosomal instability and tumorigenesis in early colorectal adenomas. PMID: 25080505
- A dominant negative effect is considered the pathogenic mechanism in SMC1A-defective female patients, the level of allelic preferential expression might be one of the factors contributing to the wide phenotypic variability observed in these patients. PMID: 24756084
- Clinical comparison between our patient with a previously reported individual with a SMC1A duplication and four male carriers of similar sSMC reported in databases, suggest that they all share clinical features related to cohesinopathies PMID: 23683030
- The mutation c.1731G>A/p.E577E in our patient expands the mutational spectrum of SMC1A to splice site mutations and also represents the first exonic synonymous splice site mutation observed in any human cohesinopathy PMID: 23863341
- Our clinical and molecular findings expand the total number of characterized SMC1A-mutated patients (from 44 to 52) and the restricted repertoire of SMC1A mutations (from 29 to 34), contributing to the molecular and clinical signature of SMC1A-based CdLS. PMID: 24124034
- Inhibiting SMC1A expression efficiently (P < 0.001) resulted in inhibiting the proliferation and colony formation of U251 and U87MG glioblastoma cells. PMID: 23754617
- Human SMC3 knock-down rendered SMC1 instable without cytoplasmic accumulation. PMID: 23776448
- studies report for the first time that SMC1 is overexpressed in TNBC cells where it plays a role in cell migration and drug sensitivity, and thus provides a potential therapeutic target for this highly invasive breast cancer subtype PMID: 23717600
- These results suggest that SMC1A upregulation is involved in the pathogenesis of glioma. PMID: 23638217
- c-MYC down-regulation caused by cohesin mutations in SMC1A and SMC3 genes may be an early/primary event in the pathogenesis of Cornelia de Lange syndrome. PMID: 23106691
- NIPBL, SMC1A, and SMC3 mutation-positive patients were equally likely to have congenital heart diseases in Cornelia de lange syndrome. PMID: 22965847
- phosphorylation of Rad50 plays a key regulatory role as an adaptor for specific ATM-dependent downstream signaling through SMC1 for DNA repair and cell cycle checkpoint control in the maintenance of genome integrity. PMID: 21757780
- phosphorylation of SMC1 is required for an increased mobility after DNA damage in G2-phase cells, suggesting that ATM-dependent phosphorylation facilitates mobilization of the cohesin complex after DNA damage PMID: 21056556
- SMC1A missense mutation is associated with Cornelia de Lange syndrome. PMID: 20635401
- Low SMC1A expression predicts poor survival in acute myeloid leukemia. PMID: 20514443
- The identification of 14 additional mutations of the cohesin complex genes NIPBL and SMC1A in a cohort of 30 unrelated patients with Cornelia de Lange syndrome, is reported. PMID: 20358602
- Interaction between Rae1 and cohesin subunit SMC1 is required for proper spindle formation. PMID: 20016259
- results suggest that mechanistically SMC1A-related Cornelia de Lange Syndrome is not due to altered levels of the SMC1A transcript, but rather that the mutant proteins maintain a residual function in males and enact a dominant negative effect in females. PMID: 19701948
- This protein is localized at the kinetochores and is involved in cell division. PMID: 12199140
- Inhibition of SMC1 is associated with chromosomal aberrations PMID: 15640246
- RPGR-ORF15, which is mutated in retinitis pigmentosa, associates with SMC1. PMID: 16043481
- Replication timing of FRA3B in G2 was studied by bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) labeling by a fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)-based approach through the analysis of clones spanning the FRA3B region. PMID: 16242161
- mutations in SMC1L1 (also known as SMC1), which encodes a different subunit of the cohesin complex, are responsible for Cornelia de Lange syndrome in three male members of an affected family and in one sporadic case PMID: 16604071
- SMC1 binding represses OARE [OA (okadaic acid) response element] activity and its dissociation allows the recruitment of CAR(constitutive active/androstane receptor) to the OARE, synergizing the expression of the CYP2B6 gene. PMID: 16623664
- nuclear exclusion is important to prevent cohesin cleavage during interphase in the absence of securin and the phosphorylation inhibition PMID: 17102637
- So far, two genes (NIPBL and SMC1L1) have been identified causing Cornelia de Lange syndrome (CdLS) or CdLS-like phenotypes. PMID: 17106445
- Mutations in SMC1A cause a mild variant of cornelia de Lange syndrome with predominant mental retardation PMID: 17273969
- The S-phase checkpoint, regulated by the ATM-p95/NBS1-SMC1 pathway, was also triggered in hypoxia/reoxygenation-exposed lymphocytes. PMID: 17544403
- identified as one of five genes containing 11 somatic mutations in a panel that included 132 colorectal cancers, then demonstrated that down-regulation of such homologs resulted in chromosomal instability and chromatid cohesion defects in human cells PMID: 18299561
- ATM plays a fundamental role in promoting the radiation-induced interaction of NBS1 with SMC1 in the presence of BRCA1, leading to the maintenance of chromosomal integrity. PMID: 18763866
- SMC1 is recruited to microtubule-bound RNA export factor 1 (Rae1) at the mitotic spindle pole. PMID: 18832153
- Cornelia de Lange syndrome mutations in SMC1A or SMC3 bind to DNA with higher affinity and display genomic instability. PMID: 18996922
顯示更多
收起更多
-
相關(guān)疾病:Cornelia de Lange syndrome 2 (CDLS2)
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Nucleus. Chromosome. Chromosome, centromere, kinetochore. Note=Associates with chromatin. Before prophase it is scattered along chromosome arms. During prophase, most of cohesin complexes dissociate from chromatin probably because of phosphorylation by PLK, except at centromeres, where cohesin complexes remain. At anaphase, the RAD21 subunit of the cohesin complex is cleaved, leading to the dissociation of the complex from chromosomes, allowing chromosome separation. In germ cells, cohesin complex dissociates from chromatin at prophase I, and may be replaced by a meiosis-specific cohesin complex. The phosphorylated form on Ser-957 and Ser-966 associates with chromatin during G1/S/G2 phases but not during M phase, suggesting that phosphorylation does not regulate cohesin function. Integral component of the functional centromere-kinetochore complex at the kinetochore region during mitosis.
-
蛋白家族:SMC family, SMC1 subfamily
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-