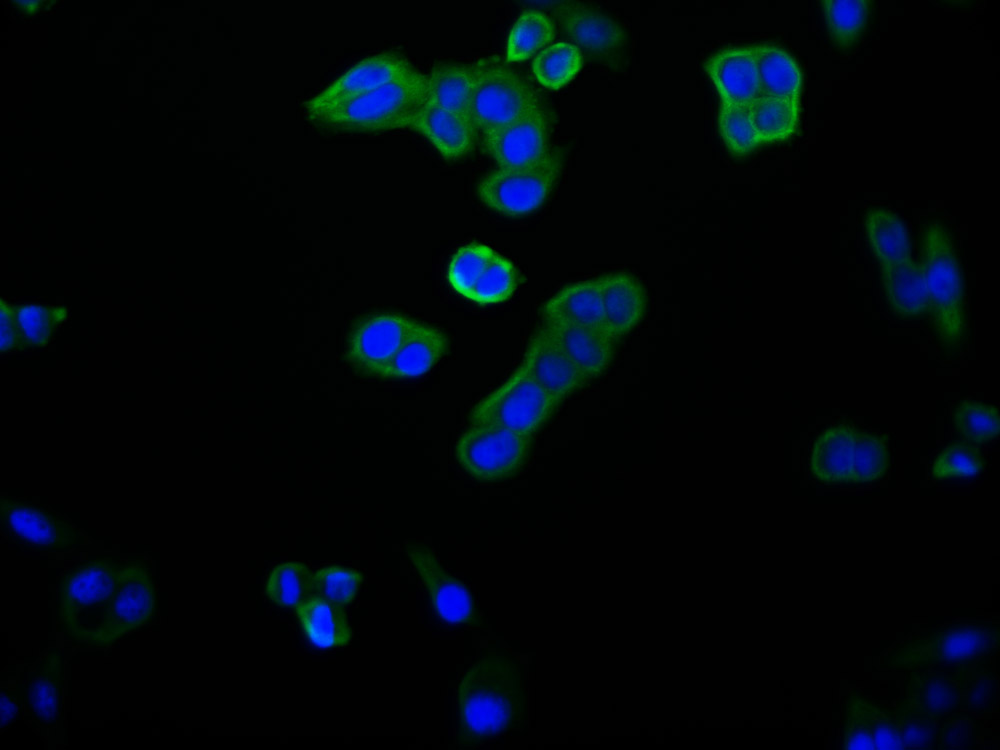
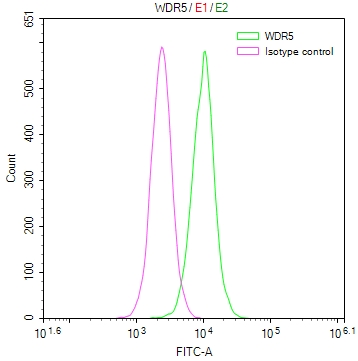
PCK1 Antibody
-
中文名稱:PCK1兔多克隆抗體
-
貨號(hào):CSB-PA923722
-
規(guī)格:¥1100
-
圖片:
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:
-
別名:cytosolic [GTP] antibody; GTP antibody; PCK1 antibody; PCKGC_HUMAN antibody; PEP carboxykinase antibody; PEPCK-C antibody; PEPCK1 antibody; PEPCKC antibody; Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1 (soluble) antibody; Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1 antibody; Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase antibody; Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, cytosolic [GTP] antibody; Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, cytosolic antibody; Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase antibody; Phosphopyruvate carboxylase antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應(yīng)種屬:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Synthetic peptide of Human PCK1
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
標(biāo)記方式:Non-conjugated
-
抗體亞型:IgG
-
純化方式:Antigen affinity purification
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:-20°C, pH7.4 PBS, 0.05% NaN3, 40% Glycerol
-
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Liquid
-
應(yīng)用范圍:ELISA,WB
-
推薦稀釋比:
Application Recommended Dilution ELISA 1:2000-1:5000 WB 1:500-1:2000 -
Protocols:
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:Cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase that catalyzes the reversible decarboxylation and phosphorylation of oxaloacetate (OAA) and acts as the rate-limiting enzyme in gluconeogenesis. Regulates cataplerosis and anaplerosis, the processes that control the levels of metabolic intermediates in the citric acid cycle. At low glucose levels, it catalyzes the cataplerotic conversion of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), the rate-limiting step in the metabolic pathway that produces glucose from lactate and other precursors derived from the citric acid cycle. At high glucose levels, it catalyzes the anaplerotic conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate to oxaloacetate. Acts as a regulator of formation and maintenance of memory CD8(+) T-cells: up-regulated in these cells, where it generates phosphoenolpyruvate, via gluconeogenesis. The resultant phosphoenolpyruvate flows to glycogen and pentose phosphate pathway, which is essential for memory CD8(+) T-cells homeostasis. In addition to the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase activity, also acts as a protein kinase when phosphorylated at Ser-90: phosphorylation at Ser-90 by AKT1 reduces the binding affinity to oxaloacetate and promotes an atypical serine protein kinase activity using GTP as donor. The protein kinase activity regulates lipogenesis: upon phosphorylation at Ser-90, translocates to the endoplasmic reticulum and catalyzes phosphorylation of INSIG proteins (INSIG1 and INSIG2), thereby disrupting the interaction between INSIG proteins and SCAP and promoting nuclear translocation of SREBP proteins (SREBF1/SREBP1 or SREBF2/SREBP2) and subsequent transcription of downstream lipogenesis-related genes.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- This study reveals a unique mechanism to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma by switching from glycolysis to gluconeogenesis through Nur77 antagonism of PEPCK1 degradation. PMID: 28240261
- circC3P1 acts as a tumor suppressor via enhancing PCK1 expression by sponging miR-4641 in hepatocellular carcinoma. PMID: 29608893
- The expression levels of PCK1 were suppressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) samples and in cells derived from HCC tissues. PMID: 29768256
- Study investigated the molecular basis of such effects focusing on a commonly studied polymorphism in pig Pgc1alpha, which changes a cysteine at position 430 (WT) of the protein to a serine (C430S); found that differential O-GlcNAcylation of Pgc1alpha regulates PCK1 activity and this molecular mechanism could explain at least in part the epistatic interaction between both genes. PMID: 28644880
- Study identified a novel homozygous PCK1 missense mutation causing cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase deficiency presenting as childhood hypoglycemia. PMID: 28216384
- HBXIP is able to depress the gluconeogenesis in hepatoma cells by suppressing PCK1 to promote hepatocarcinogenesis, involving miR-135a/FOXO1 axis and PI3K/Akt/p-FOXO1 pathway. PMID: 27609066
- an extended binding site in the catalytic cleft of cPEPCK which is used by 3-MPA to inhibit cPEPCK non-competitively. PMID: 26528723
- A mutation of PCK1 associated with Smith-Magenis Syndrome, cytosolic PEPCK deficiency and NMDA receptor glutamate insensitivity. PMID: 24863970
- Insulin-dependent translocation of FOXO1 regulated transcriptional repression of PCK1 concomitant with the formation of the FOXO1-euchromatic histone-lysine N-methyltransferase2 (EHMT2) complex and histone modifications of the PCK1 promoter region PMID: 25736587
- Lipopolysaccharide and monophosphoryl lipid A also up-regulated G6PC and PCK1 transcript abundance in a TLR4-dependent manner. PMID: 23465595
- The PCK1 tag-single nucleotide polymorphisms influenced insulin resistance by interacting with plasma n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids levels in metabolic syndrome patients. PMID: 23092637
- HCV core protein expression-mediated FOXO1 activation and the increased PGC-1alpha leaded to the elevation of PCK1 at the mRNA level PMID: 22489460
- Acetylation regulates the stability of the gluconeogenic rate-limiting enzyme PEPCK1. PMID: 21726808
- Data show PEPCK-C and CPT-1 mRNAs are more abundant in non-tumoral tissues than in the tumoral counterpart, whereas the opposite occurred for the FAS gene. PMID: 20691246
- Studies demonstrate the association between PCK1 and smaller average brain volume. PMID: 21152065
- Study in the EYHS cohort failed to identify an association of PCK1 polymorphisms with obesity, physical activity, and fitness. PMID: 20134411
- crystal structure of human cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase reveals a new GTP-binding site PMID: 11851336
- Conserved amino acids within CCAAT enhancer-binding proteins (C/EBP(alpha) and beta) regulate gene expression PMID: 11997389
- promoter context may influence which domains within a transcription factor are employed to mediate transactivation of PEPCK PMID: 12237288
- the PGC- 1-regulated phospho(enol)pyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) promoter is a novel target promoter for SHP inhibition PMID: 12324453
- transcription of the gene for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) in the liver is regulated by SREBP-1c and Sp1 PMID: 14744869
- Promoter single nucleotide polymorphism in PCK1 was resistant to down-regulation by insulin in vitro and associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. PMID: 14764811
- PCK1 has been implicated as one of many genes associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus [review] PMID: 15046742
- AUF1 binds to multiple destabilizing elements within the 3'-UTR that participate in the rapid turnover of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase mRNA. PMID: 15951444
- The multiple instability elements present within the 3'-UTR may function synergistically to mediate both the rapid degradation and the cAMP-induced stabilization of PEPCK mRNA. The latter process may result from a PKA-dependent phosphorylation of AUF1. PMID: 16144962
- Subjects with the PCK1-232G/G genotype had more carotid IMT (0.80+/-0.02 versus 0.73+/-0.03 mm; P=0.007) but less TPV (0.10+/-0.09 versus 0.38+/-0.13; P=0.03) than subjects with other genotypes. PMID: 16282543
- Significant association of single nucleotide polymorphism within three genes--PPARgamma, SOS2, and PCK1--with Alzheimer's disease, was confirmed. PMID: 17440948
- IFN-gamma exerts a tissue-specific action in rodents and humans, having glyceroneogenesis and the PEPCK-C gene as selective targets to intensify fatty acids release from adipocytes PMID: 17495004
- The effects of several variants of retinoic acid on the expression and activity of PEPCK in human, mouse, and rat adipose tissue are reported. PMID: 18492826
- Reduced CREB phosphorylation (Ser-129) associated with inactivation of GSK3beta by Ser-9 phosphorylation may be the major mechanism underlying PEPCK-C gene suppression by AMPK-activating agents such as biguanide PMID: 18801732
- The aromatic ring of Tyr235 in PEPCK helps to position PEP in the active site and the hydroxyl group allows an optimal PEP-Mn(2+) distance for efficient phosphoryl transfer and overall catalysis. PMID: 19021757
- Val184 of PCK1 gene might increase the risk of type 2 diabetes in eastern Chinese population with BMI<23 kg/m(2) via reducing the PEPCK-C activity. PMID: 19070910
- Study validated a predicted SP1 binding site in the control of PCK1 transcription using gel shift and reporter assays. PMID: 19329064
- study is the first to investigate the association between variants of the PCK1 gene and type 2 diabetes in South Asians PMID: 19725958
顯示更多
收起更多
-
相關(guān)疾病:Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase deficiency, cytosolic (PCKDC)
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Cytoplasm, cytosol. Endoplasmic reticulum.
-
蛋白家族:Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase [GTP] family
-
組織特異性:Major sites of expression are liver, kidney and adipocytes.
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-