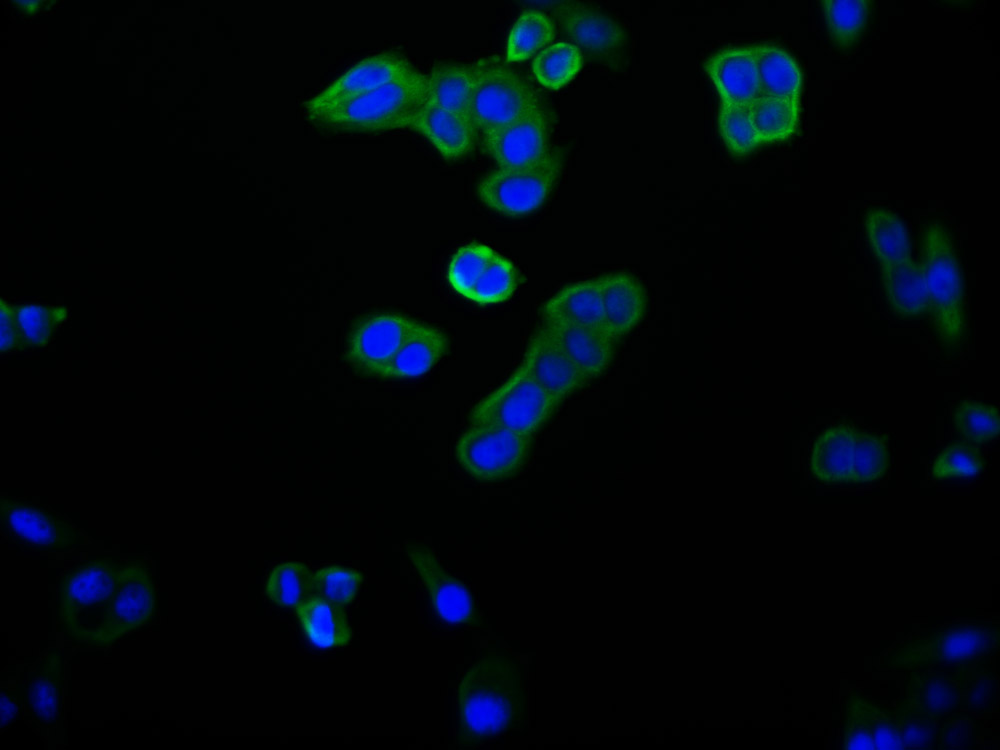
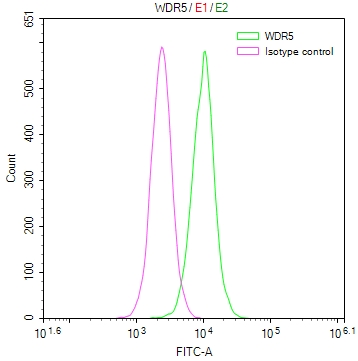
FFAR1 Antibody, FITC conjugated
-
中文名稱:FFAR1兔多克隆抗體, FITC偶聯(lián)
-
貨號(hào):CSB-PA008604LC01HU
-
規(guī)格:¥880
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
產(chǎn)品名稱:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) FFAR1 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:
-
別名:FFAR1; GPR40; Free fatty acid receptor 1; G-protein coupled receptor 40
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應(yīng)種屬:Human
-
免疫原:Recombinant Human Free fatty acid receptor 1 protein (143-178AA)
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
標(biāo)記方式:FITC
-
克隆類型:Polyclonal
-
抗體亞型:IgG
-
純化方式:>95%, Protein G purified
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4 -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Liquid
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:G-protein coupled receptor for medium and long chain saturated and unsaturated fatty acids that plays an important role in glucose homeostasis. Fatty acid binding increases glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, and may also enhance the secretion of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). May also play a role in bone homeostasis; receptor signaling activates pathways that inhibit osteoclast differentiation. Ligand binding leads to a conformation change that triggers signaling via G-proteins that activate phospholipase C, leading to an increase of the intracellular calcium concentration. Seems to act through a G(q) and G(i)-mediated pathway. Mediates the anti-inflammatory effects of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) via inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- Study reports the 2.76-A crystal structure of human GPR40 complexed with compound 1 bound in a second structurally distinct allosteric site, located at the receptor side facing the membrane lipophilic environment. Binding of compound 1 stabilizes the intracellular loop 2 (ICL2) of GPR40 in a helical conformation. Mutagenesis studies in ICL2 shows that this loop is important for Gs alpha subunit coupling. PMID: 29695780
- Data indicate that 20-HETE and FFAR1 function together in a positive feedback loop to enhance glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS). PMID: 29330456
- Comparison with an additional 2.2-A structure of the human GPR40-MK-8666 binary complex reveals an induced-fit conformational coupling between the partial agonist and AgoPAM binding sites, involving rearrangements of the transmembrane helices 4 and 5 (TM4 and TM5) and transition of the intracellular loop 2 (ICL2) into a short helix. PMID: 28581512
- Results show that GPR40 negatively regulated the cell motile and invasive activities of HT1080 cells suggesting that GPR40 negatively regulates the tumor progression of fibrosarcoma cells. PMID: 26331585
- Brain free long-chain fatty acids-GPR40/FFA1 signaling might have an important role in the modulation of endogenous pain control systems. (review) PMID: 28154332
- It regulates insulin secretion in pancreatic beta-cells. (review) PMID: 26028412
- Data from molecular docking simulations suggest that the binding pocket of GPR40 exhibits binding of free fatty acids (FFA) with chain lengths of C15 or fewer; for FFA with lengths longer than C15, part of alkyl chain extends out of binding pocket. PMID: 26974599
- GPR120 negatively and GPR40 positively regulate cellular functions during tumor progression in lung cancer cells. PMID: 26968637
- These data demonstrate that R104 in GPR40 is critically involved in the normal receptor functions. Interestingly, R104P is a registered single-nucleotide polymorphism of GPR40. PMID: 26505901
- Characterizing pharmacological ligands to study the long-chain fatty acid receptors GPR40/FFA1 and GPR120/FFA4 PMID: 25131623
- results suggest that FFAR1 is the functionally dominant free fatty acid receptor in both human and guinea pig airway smooth muscle. PMID: 26342087
- upregulation of GPR40 expression enhances the mitogenic response to epoxyeicosatrienoic acids PMID: 25679385
- Palmitic acid boosted inflammatory response of microvascular endothelial cells to LPS via GPR40 and nSMase. PMID: 25795558
- knocking down the expression of the regulatory subunit PKAR1alpha, thereby reproducing the effects of IL-1beta and PGE on VSMCs, we demonstrated the contribution of PKA activity to the observed behavior of VSMCs PMID: 26408932
- These results suggest that distinct effects of GPR120 and GPR40 are involved in the acquisition of malignant property in pancreatic cancer cells. PMID: 26282200
- GPR40 functions via both G protein-mediated and beta-arrestin-mediated mechanisms; endogenous and synthetic ligands differentially engage these pathways to promote insulin secretion. PMID: 26157145
- GPR40 and PPARgamma can function as an integrated two-receptor signal transduction pathway, a finding with implications for rational antidiabetic drug development. PMID: 26105050
- the activation of GPR40 attenuates cisplatin-induced apoptosis. PMID: 25092426
- arrestin-3 and GRK2 play an essential role in the regulation of agonist-mediated GPR40 internalization, but are not involved in the regulation of constitutive GPR40 internalization. PMID: 25038452
- In a neuroblastoma cell line, GPR40 was activated by docosahexaenoic acid and selective agonists, yet not by palmitic acid. Its activation provoked the phosphorylation of CREB. PMID: 24550142
- the crystal structure of hGPR40 receptor bound to TAK-875 at 2.3 A resolution PMID: 25043059
- Potent free fatty acid 1 receptor agonist TUG-469 may be promising candidate for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. PMID: 23861168
- It was concluded that FFAR1 in the pancreatic beta-cell plays a substantial role not only in acute potentiation of insulin secretion by palmitate but also in the negative long-term effects of palmitate on insulin metabolism. PMID: 24035997
- FFAR1 agonists support beta-cell function, but variation in FFAR1 influences NEFA effects on insulin secretion and therefore could affect therapeutic efficacy of FFAR1 agonists. PMID: 23378609
- A review of the physiological role of GPR40 and potential antidiabetic drugs targeting GPR40. [Review] PMID: 23023155
- Propionate-stimulated GPR41 strongly coupled to ERK1/2 activation, while the coupling of linoleic acid-activated GPR40 and acetate-activated GPR43 was weaker. PMID: 22712802
- GPR41 gene expression is mediated by internal ribosome entry site (IRES)-dependent translation of bicistronic mRNA encoding GPR40 and GPR41 proteins PMID: 22493486
- Phytanic acid and pristanic acid activate the free fatty acid receptor GPR40, a G-protein-coupled receptor which is involved in the Ca2+ signaling of fatty acids. PMID: 21570468
- GPR40/FFA1 influences both insulin and glucagon secretion in rat islets, but only insulin secretion in human islets. PMID: 22106100
- differences in body composition and lipids associated with common SNPs in the FFAR1 gene PMID: 21552566
- Results describe agonist-receptor interactions of GPR40 using molecular dynamics simulations. PMID: 20227312
- results show expression of GPR40 in pancreatic islets which are regulated by FFA; finding that T2DM islets have lower GPR40 expression & correlation with insulin secretion raises possibility of involvement of GPR40 in diabetes beta-cell dysfunction PMID: 19758793
- Free fatty acids regulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells through GPR40 PMID: 12629551
- Results suggest that GPR40 is implicated in the control of breast cancer cell growth by fatty acids and that GPR40 may provide a link between fat and cancer. PMID: 15695516
- results suggest that the Arg211His polymorphism in the GPR40 protein gene may contribute to the variation of insulin secretory capacity in Japanese men PMID: 15736105
- study provides evidence for GPR40 gene expression in pancreatic beta cells and implicates GPR40 in insulin secretion in humans. PMID: 16525841
- GPR40 responded to fatty acids with different on-rates, and could be occupied by endogenous agonists before assay, masking the pharmacology of the receptor PMID: 17200419
- cell-specific expression of the GPR40 gene involves a characteristic chromatin organization of the locus and is controlled at the transcriptional level through HR2, a potent beta cell-specific enhancer PMID: 17525159
- analysis of residues important for agonist recognition and activation in GPR40 PMID: 17699519
- Variation in the FFAR1 gene may contribute to impaired beta cell function in type 2 diabetes PMID: 17987108
- This newly identified GPR40 variant results in a loss of function that prevents the beta-cell ability to adequately sense lipids as an insulin secretory stimulus because of impaired intracellular Ca2+ concentration increase. PMID: 18583466
- A flow cytometry-based binding assay for FFAR1 is reported. PMID: 18927207
- In this review, the mechanism of receptor activation, pharmacology, and the physiological functions of the fatty acid binding receptors GPR40, GPR41, GPR43, and GPR119 are discussed. PMID: 19009545
- Two arginine-glutamate ionic locks near the extracellular surface of FFAR1 gate receptor activation. PMID: 19068482
- Transfection of GPR40 into mice may provide a novel insulin secretagogue beneficial for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. PMID: 19401434
- This paper predicts the 5' structure of the human GP40 gene based on alignments between mouse and human genomic DNA. PMID: 17525159
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:G-protein coupled receptor 1 family
-
組織特異性:Detected in brain and pancreas. Detected in pancreatic beta cells.
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
-
-
-
-
-