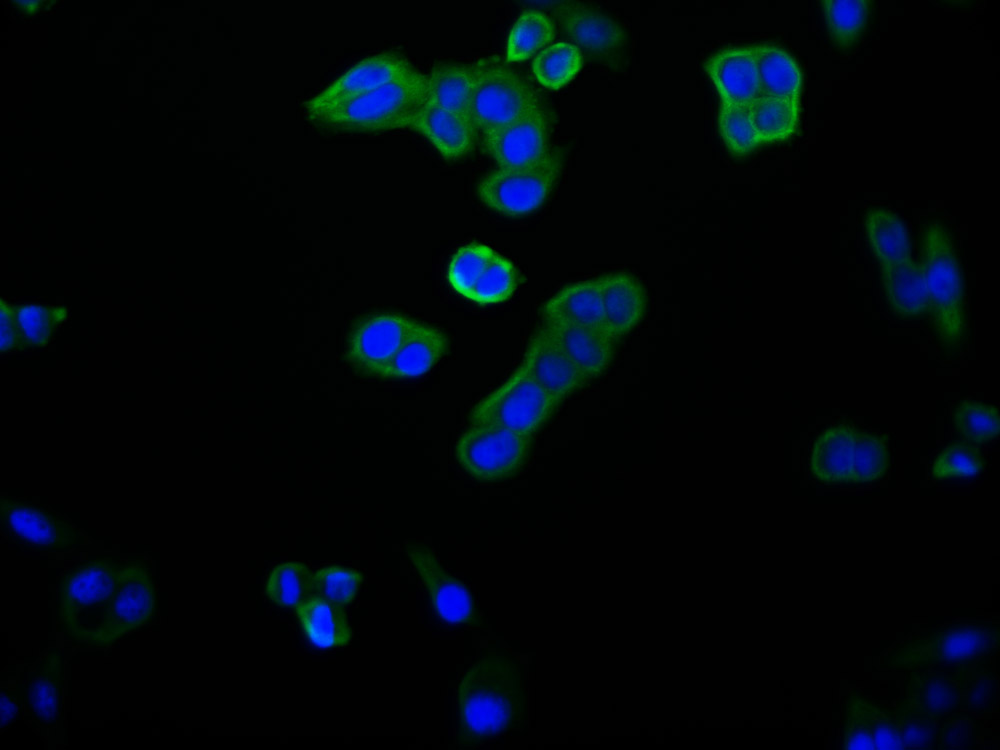
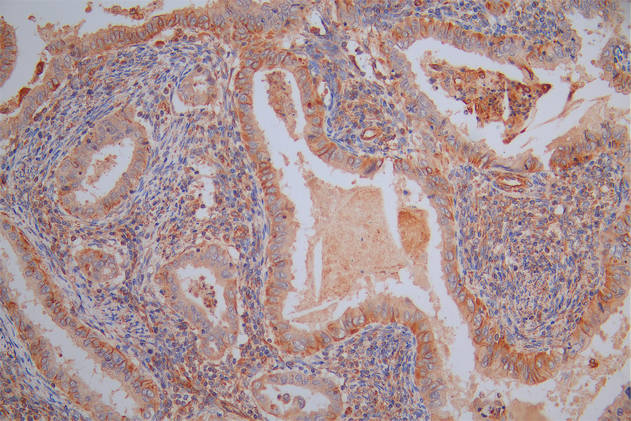
CD69 Antibody
-
中文名稱:CD69兔多克隆抗體
-
貨號(hào):CSB-PA001473
-
規(guī)格:¥880
-
圖片:
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:
-
別名:Activation inducer molecule (AIM/CD69) antibody; Activation inducer molecule antibody; AIM antibody; BL-AC/P26 antibody; BLAC/P26 antibody; C-type lectin domain family 2 member C antibody; CD69 antibody; CD69 antigen (p60; early T-cell activation antigen) antibody; CD69 antigen antibody; CD69 molecule antibody; CD69_HUMAN antibody; CLEC2C antibody; EA1 antibody; Early activation antigen CD69 antibody; Early lymphocyte activation antigen antibody; Early T cell activation antigen p60 antibody; Early T-cell activation antigen p60 antibody; GP32/28 antibody; Leu23 antibody; Leukocyte surface antigen Leu-23 antibody; MLR-3 antibody; MLR3 antibody; VEA antibody; Very Early Activation Antigen antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應(yīng)種屬:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of Human CD69.
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
標(biāo)記方式:Non-conjugated
-
抗體亞型:IgG
-
純化方式:The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
-
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Liquid
-
應(yīng)用范圍:WB, ELISA
-
推薦稀釋比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:2000 ELISA 1:40000 -
Protocols:
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:Involved in lymphocyte proliferation and functions as a signal transmitting receptor in lymphocytes, natural killer (NK) cells, and platelets.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- CD69 is a direct target of miR-367-3p. PMID: 30015935
- The frequency of CD69+ T cells was significantly higher in CD8+ and CD4+ T cells in nasal polyps compared with the peripheral blood of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. PMID: 29749428
- this paper shows that decrease of CD69 levels on TCR Valpha7.2(+)CD4(+) innate-like lymphocytes is associated with impaired cytotoxic functions in chronic hepatitis B virus-infected patients PMID: 28606013
- AIM expression in the kidney was associated with urinary protein and decline in kidney function. PMID: 26846784
- Higher CD69 expression were less sensitive to bendamustine and is associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. PMID: 26701728
- In vitro functional assays showed that CD69(+) Treg cells exerted an important suppressive effect on the activation of T effector cells PMID: 26100786
- results demonstrate the functional and mechanistic interplays between CD69 and S100A8/S100A9 in supporting Treg-cell differentiation PMID: 26296369
- Elevated expression of CD69 and CD161 on NK cells can be considered as immunological risk markers in RSA and IVF failure. PMID: 24975965
- these findings identify CD69 and galectin-1 to be a novel regulatory receptor-ligand pair that modulates Th17 effector cell differentiation and function. PMID: 24752896
- REVIEW: CD69 exerts a complex immunoregulatory role in humans, and that it could be considered as a target molecule for the therapy of immune-mediated diseases PMID: 23954168
- Following coculture with GTKO/CD46 pig mesenchymal stromal cells, it is possible that upregulation of CD69 on human T cells initiates signaling events that would regulate CD4+ and CD8+ T cell activation and differentiation. PMID: 24044963
- In patients with allergic rhinitis CD69 antigen is overexpressed on human peripheral blood natural killer cells reflecting their activation status. PMID: 23454781
- This is the first report of the regulation of CD69 expression by LMP-1, and this novel finding may, thus, represent an important link between the EBV oncoprotein LMP-1 and its critical role in the development of EBV-associated diseases. PMID: 23546309
- CD69 is induced by integrin alpha4beta1 outside-in signalling and T-cell receptor signalling. PMID: 23758320
- CD69 overexpression is associated with the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 infection and adult T-cell leukemia. PMID: 23507197
- Intron I acts as an important regulatory element of CD69 expression. PMID: 22456278
- CD69 is significantly correlated with poor clinical and biological prognostic factors and is confirmed to be an independent disease prognosticator in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. PMID: 21993667
- Priming with apoptotic debris prevented DCs from establishing cytotoxicity toward live human tumor cells by inducing a Treg-cell population, defined by coexpression of CD39 and CD69 PMID: 22678911
- T cells isolated from the hepatocellular carcinoma tissues expressed significantly more CD69 molecules than did those on paired circulating and nontumor-infiltrating T cells; these tumor-derived CD69(+) T cells could induce considerable IDO in monocytes PMID: 22184722
- Results suggest that H. pylori induces CD69 expression through the activation of NF-kappaB, and that cagPAI might be relevant in the induction of CD69 expression in T cells. CD69 in T cells may play a role in H. pylori-induced gastritis. PMID: 21990950
- Caffeine does not appear to depress Natural killer cell CD69 expression. PMID: 21152932
- Studies provide a mechanistic link between CD69 and the regulation of T(H)17 responses. PMID: 21427408
- The expression of CD69 in T lymphocytes from nasal polyps was abnormally high. PMID: 15952571
- structure refined to 1.37 A resolution provides further details of the overall structure and the asymmetric interface between the monomers in the native dimer PMID: 20054122
- analysis of CD69 molecules on human CD4+ T cell membrane PMID: 19670272
- CD69 engagement initiates protein tyrosine kinase-dependent signaling pathways in IL-2-activated NK cells by inducing selective activation of Syk, but not ZAP70, kinase. PMID: 12077230
- CD69 transduces a Bcl-2-dependent death signal when ligated by a specific antibody. As the function of CD69 appears to be restricted to activated eosinophils, making an ideal target for therapeutic intervention in asthma. PMID: 12234263
- a higher CD69 expression when atopic neutrophils were incubated with GM-CSF compared to non-atopic neutrophils PMID: 12540017
- GM-CSF, IFN-gamma or IFN-alpha significantly induced CD69 expression on neutrophils. We demonstrated the capacity of CD69 to act as a costimulus for TNF-alpha production by neutrophils. PMID: 12718936
- expression of CD69 on CD3+ and CD8+ peripheral blood T cells correlates closely with the presence of acute graft rejection in renal allograft recipients PMID: 12865808
- Increased CD69 of T lymphocytes, along with abnormally elevated immunologically active molecules play an important role in immune pathogenesis of patients with myelodysplastic syndrome(MDS). PMID: 14728878
- CD69 forms a complex with and negatively regulates S1P1 and that it functions downstream of IFN-alpha/beta, and possibly other activating stimuli, to promote lymphocyte retention in lymphoid organs PMID: 16525420
- Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein II reduces CD69 expression in T cells. PMID: 16788832
- data suggest unidentified natural ligands for CD69 and/or CD69 autoantibodies possibly affect joint-composing cell types through increased production of S100A9 in neutrophils, providing insight into functions of CD69 on neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis PMID: 17237603
- IL-3 is a central inducer of CD69 expression. Upregulated CD69 expression on locally accumulated basophils in bronchial asthma may be partly due to a combination of local cytokines, especially IL-3, plus IgE-cross-linking allergens. PMID: 17541278
- Since induction of CD69 surface expression is dependent on the activation of the protein kinase C (PKC) activation pathway, it is suggested that in chronic fatigue syndrome there is a disorder in the early activation of the immune system involving PKC. PMID: 17693977
- results do not support a major role for the CD69 gene polymorphisms in RA genetic predisposition in our population. PMID: 18627570
- the physical, biochemical and in vivo characteristics of a highly stable soluble form of CD69 obtained by bacterial expression of an appropriate extracellular segment of this protein. PMID: 18959746
- Expression of CD69 and IL8 is upregulated upon Bcr-Abl expression PMID: 19383348
- soluble factors in SSc plasma inhibit Treg function specifically that is associated with altered Treg CD69 and TGFbeta expression PMID: 19543397
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein.
-
組織特異性:Expressed on the surface of activated T-cells, B-cells, natural killer cells, neutrophils, eosinophils, epidermal Langerhans cells and platelets.
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-