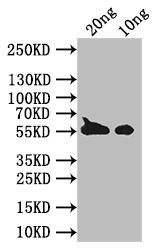
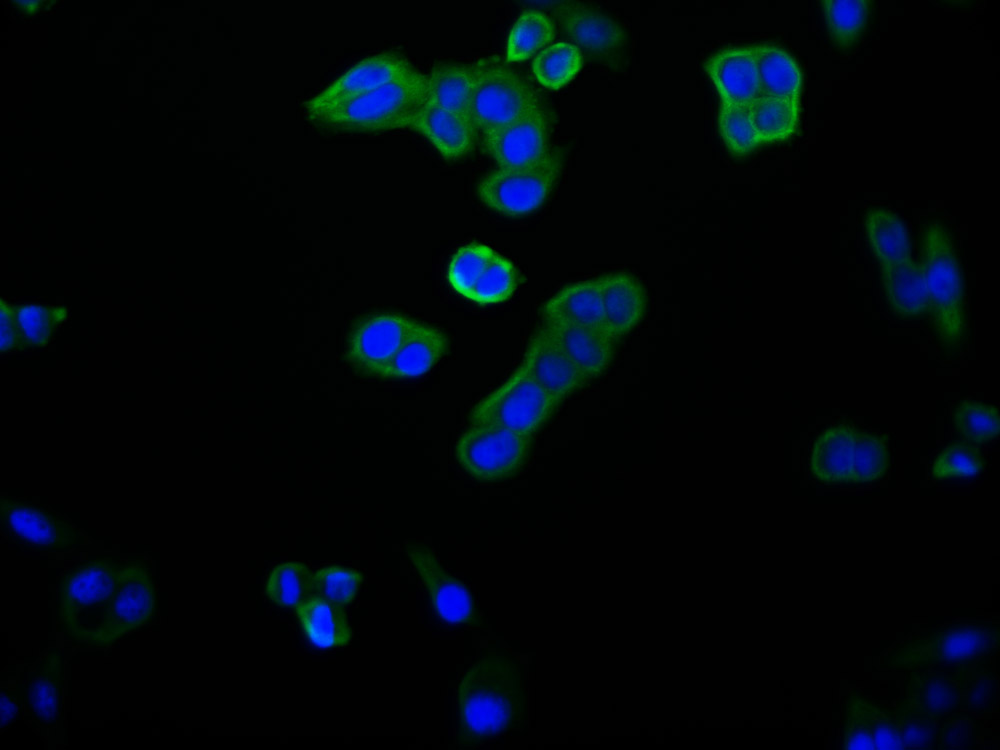
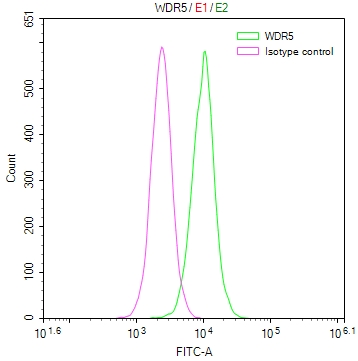
BZLF1 Antibody
-
中文名稱:BZLF1兔多克隆抗體
-
貨號(hào):CSB-PA355980ZA01EFA
-
規(guī)格:¥660
-
促銷:
-
圖片:
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:BZLF1
-
別名:BZLF1 antibody; Trans-activator protein BZLF1 antibody; EB1 antibody; Zebra antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應(yīng)種屬:Epstein-Barr virus
-
免疫原:Recombinant Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 protein
-
標(biāo)記方式:Non-conjugated
-
克隆類型:Polyclonal
-
抗體亞型:IgG
-
純化方式:>95%, Protein G purified
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300 Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4
-
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Liquid
-
應(yīng)用范圍:ELISA, WB
-
推薦稀釋比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:2000 -
Protocols:
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:Plays a key role in the switch from latent infection to lytic cycle producing new virions. Acts as a transcription factor, inducing early lytic cycle genes, and as a origin binding protein for genome replication. BZLF1 activates the promoter of another EBV gene (BSLF2+BMLF1).
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- position C189 in Zta impacts sequence-specific binding to DNA containing modified and unmodified cytosine. PMID: 29772230
- ERK/c-Jun recruits Tet1 to Induce Zta expression and Epstein-Barr virus reactivation through DNA demethylation. PMID: 27708396
- HIF-1alpha directly bound the promoter of the EBV primary latent-lytic switch BZLF1 gene, Zp, activating transcription via a consensus hypoxia-response element (HRE) located at nt -83 through -76 relative to the transcription initiation site. PMID: 28617871
- By CRISPR/Cas9-induced inactivation of TLR9, MyD88, IRAK4 and IRAK1 we confirm that BZLF1 repression is dependent on functional TLR9 and MyD88 signaling, and identify IRAK4 as an essential element for TLR9-induced repression of BZLF1 expression upon BCR cross-linking PMID: 29088270
- Comparison of how AP-1 (Jun/Jun dimer) and Epstein-Barr virus Zta recognize methyl groups within their cognate response elements PMID: 28158710
- Binding of PARP1 at the BZLF1 lytic switch promoter restricts Epstein Barr Virus reactivation. PMID: 28456021
- These results suggest that lytic Epstein-Barr virus infection attenuates the transmission of inflammatory paracrine senescence through BZLF1 downregulation of TNF-alpha secretion and alters the inflammatory microenvironment to allow virus propagation and persistence. PMID: 27334596
- The dimerization region of Epstein-Barr virus Zta is not required to mediate host CIITA repression. PMID: 26653871
- These results suggest that Epstein-Barr Virus BZLF1 attenuates the proinflammatory responses to facilitate viral replication. PMID: 26537683
- Presented is a model of DNA damage responses activation during the EBV lytic cycle in which ZEBRA induces ATM kinase phosphorylation, in a DNA binding dependent manner, to modulate gene expression. PMID: 25950714
- RanBPM was found to enhance Zta-dependent transcriptional activity via the inhibition of Zta sumoylation. PMID: 25900136
- Studied the effects of BZLF1 on cellular response to DNA damage in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. PMID: 26006018
- This is the first report to characterize BZLF1 gene polymorphisms in paediatric patients from our geographical region and to suggest the association of these polymorphisms with malignant lymphomas. PMID: 24666405
- ZEBRA and BGLF5 each function as viral host shutoff factors. PMID: 24705134
- these results indicate a critical role for MCAF1 in AP-1-dependent Rta activation of BZLF1 transcription. PMID: 24598729
- Performed the recombinant production of a biologically active Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 trans-activator, i.e., Z-encoded broadly reactive activator (ZEBRA), that recognized specific DNA motifs. PMID: 24291446
- B-cell specific transcription factor, Oct-2, inhibits the function of the viral immediate-early protein, BZLF1, and prevents lytic viral reactivation. PMID: 22346751
- the genetic characteristics of BZLF1 gene and its promoter Zp of the epidemic strains in children with primary Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated diseases PMID: 24772891
- TAF-Ibeta promotes BZLF1 expression and subsequent lytic infection by affecting chromatin at the BZLF1 promoter PMID: 23691099
- Mutation of MEF2 sites severely impaired both spontaneous and induced expression of not only BZLF1, but also BRLF1 in comparison to wild-type or revertant virus cases. PMID: 23843637
- The B-cell-specific transcription factor and master regulator Pax5 promotes Epstein-Barr virus latency by negatively regulating the viral immediate early protein BZLF1. PMID: 23678172
- Zta drives cell migration and invasion through MMPs PMID: 23409137
- BZLF1 is a pioneer factor that reverses epigenetic silencing of viral DNA to allow escape from latency. PMID: 22969425
- Genome-wide analyses of Zta binding to the Epstein-Barr virus genome reveals interactions in both early and late lytic cycles and an epigenetic switch leading to an altered binding profile. PMID: 23015699
- The mechanism of p53-mediated Epstein-Barr viral Zta protein activation requires the cooperative action of another cellular factor, Sp1. PMID: 22711357
- Herpes simplex virus type 1 induces the reactivation of latent EBV by triggering BZLF1 expression. PMID: 22188237
- Epigenetic modification of the BZLF1 promoter in latent Raji cells by histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3), H3K9me2/me3, and H4K20me3. PMID: 22357272
- The authors show that expression of the Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early protein BZLF1 is restricted to Blimp1-positive epithelial cells in oral hairy leukoplakia. PMID: 22278826
- The abundance of Zta protein coupled with the methylation status of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome act together to co-ordinate the expression of lytic cycle genes at the majority of EBV promoters. PMID: 22022468
- conclude that TGF-beta induces EBV lytic reactivation via the canonical Smad pathway by activating BZLF1 gene expression through multiple SBEs acting in concert PMID: 21593157
- study reports that specific single missense mutations within the basic domain of ZEBRA induce the formation of nuclear aggresomes, which strongly sequester the mutant protein PMID: 21233201
- The authors conclude that the ZIIR element is a potent silencing element in the BZLF1 promoter Zp and plays a key role in establishment and maintenance of virus latency by inhibiting activation of Zp through the PKC signal transduction pathway. PMID: 21389123
- This study also reveals that the interaction between Zta and Ku80 involves the C-terminal region of Zta and the 425 aa N-terminal region of Ku80. PMID: 21123545
- Data show that Daudi cells express glucocorticoid receptors that mediate Dex-dependent up-regulation of BZLF1 mRNA levels. PMID: 20466055
- By a chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay, the authors show that Ubn-1 blocks EB1-human herpesvirus 4 DNA interaction. PMID: 21084479
- These observations indicate that the EBV lytic transactivator protein Zta displays activity consistent with a pathogenic role in pulmonary fibrosis associated with herpesvirus infection. PMID: 20817778
- Results strongly suggest that oxidative stress contributes to the reactivation of EBV lytic cycle, through induction of BZLF-1 gene expression. PMID: 19898754
- Enhanced binding of ZEBRA to the origin of lytic DNA replication is crucial for lytic viral DNA replication. PMID: 20808903
- Data propose that EBV protein Zta activates SOCS3 protein as an immune escape mechanism that both suppresses optimal IFNalpha secretion by human monocytes and favors a state of type I IFN irresponsiveness in these cells. PMID: 20689596
- sumoylation of BZLF1 regulates its transcriptional activity through histone modification during Epstein-Barr virus productive replication PMID: 20516063
- Study renders ZEBRA-MD a promising candidate for therapeutic protein delivery applications. PMID: 20385549
- These data suggest that Zta acts by inducing and/or stabilizing a DNA hairpin structure during productive infection. PMID: 20444899
- viral BZLF1 protein is crucial both to establish latency and to escape from it; Epstein Barr virus has evolved to its host mode of dna methylation. PMID: 20080764
- Our work implies that the balance of promyelocytic leukemia protein and BZLF1 levels in cells may affect how each protein functions. PMID: 16307818
- there are three phosphorylation sites on the Epstein-Barr virus ZEBRA protein PMID: 16321978
- Results describe the crystal structure of ZEBRA's DNA binding domain bound to an Epstein-Barr virus lytic gene promoter element. PMID: 16483937
- Comparison among viral orthologues of Zta suggest that a conserved N-terminal extension of the consensus B-ZIP domain is required for this multivalent DNA recognition capacity of Zta and is essential for viral reactivation.[Zta] PMID: 16971443
- BZLF1 is expressed as an immediate-early gene following primary EBV infection of B lymphocytes. PMID: 17079287
- We report that the plasma cell differentiation factor, XBP-1s, activates the expression of the master regulator of EBV lytic activation, BZLF1. PMID: 17898050
- HHV8-RTA and EBV-BZLF1 are co-localized and physically interact with each other in dually-infected PELs, required for the mutual inhibition of the two molecules PMID: 18253508
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Host nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:BZIP family
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)鏈接:
KEGG: vg:3783744
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-