Recombinant Mouse Interleukin-22 protein (Il22)
In Stock產(chǎn)品詳情
-
純度:>96% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
內(nèi)毒素:Less than 1.0 EU/μg as determined by LAL method.
-
生物活性:Fully biologically active when compared to standard. The ED50 as determined by inducing IL-10 secretion of human COLO 205 cells is less than 0.2 ng/ml, corresponding to a specific activity of >5.0x106 IU/mg.
-
基因名:Il22
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Il22; Il22a; Iltif; IltifaInterleukin-22; IL-22; IL-10-related T-cell-derived-inducible factor; IL-TIF; IL-TIF alpha; Interleukin-22a; IL-22a
-
種屬:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白長(zhǎng)度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
來(lái)源:E.Coli
-
分子量:16.6 kDa
-
表達(dá)區(qū)域:34-179aa
-
氨基酸序列LPVNTRCKLE VSNFQQPYIV NRTFMLAKEA SLADNNTDVR LIGEKLFRGV SAKDQCYLMK QVLNFTLEDV LLPQSDRFQP YMQEVVPFLT KLSNQLSSCH ISGDDQNIQK NVRRLKETVK KLGESGEIKA IGELDLLFMS LRNACV
-
蛋白標(biāo)簽:Tag-Free
-
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
緩沖液:0.2 μm filtered PBS, pH 7.4 ,lyophilized
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:5-10 business days
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:Cytokine that contributes to the inflammatory response in vivo.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- The level of anti-IL17A autoantibodies that develop in aged Aire-deficient mice is not sufficient for conferring susceptibility to oropharyngeal candidiasis. However, patient-derived monoclonal antibodies that cross-react with murine IL-22 increase the fungal burden on C. albicans infected mucosa. PMID: 29150834
- This study defines a critical IL-36/IL-23/IL-22 cytokine network instrumental for antimicrobial peptide production and host defense in intestinal mucosa damage using a mouse inflammatory bowel disease model. PMID: 29760082
- The level of lncRNA H19 is increased in inflamed intestinal tissues from mice and patients. The inflammatory cytokine IL22 induces expression of H19 in IECs, which is required for intestinal epithelial proliferation and mucosal healing. H19 lncRNA appears to inhibit p53 protein and microRNA 34a and let-7 to promote proliferation of IECs and epithelial regeneration. PMID: 29621481
- Despite the presence of all Notch pathway molecules in the kidney and a model-specific induction of Notch ligands, IL-22 was only up-regulated in acute inflammation, but rapidly down-regulated during regeneration. This implies that for targeting injury responses, e.g. via IL-22, species-specific differences, injury type and time points have to be considered. PMID: 29054964
- Knockout of signal transducer and activator of transcription factor-3 (STAT3) in intestine epithelial cells resulted in complete loss of IL-22 protection, demonstrating that STAT3 is required for intestine barrier protection following ethanol combined with injury. PMID: 28498296
- Cancer cells induce IL-22 production from memory CD4(+) T cells via activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and the release of IL-1beta to promote tumor growth. PMID: 29150554
- although IL-22 is expressed, it seems to play a minor role in protection and pathology during the acute systemic infection with the reticulotropic Tulahuen strain of T. cruzi PMID: 27650379
- IL-22 amplifies the inflammatory response, induces endothelial dysfunction and promotes blood pressure elevation in angiotensin II-induced hypertensive mice via STAT3 signaling. PMID: 28974499
- these results demonstrate a strong association between Hh-induced DNA damage and the development of dysplasia, and further suggest that IL-22-dependent induction of iNOS within crypt epithelial cells rather than macrophages is a driving force in this process PMID: 28198364
- IL-22 plays an important role in CIA development, and neutralizing this cytokine seems an attractive new strategy in RA treatment. Most importantly, SPECT/CT imaging with 111In-28H1 can be used to specifically monitor therapy responses, and is potentially more sensitive in disease monitoring than the gold standard method of macroscopic arthritis scoring. PMID: 29361119
- Protease IV, is responsible for the degradation of IL-22 by P. aeruginosa. The major anti-proteases molecules present in the lungs were unable to inhibit protease IV enzymatic activity. This so far undescribed cleavage of IL-22 by a bacterial protease is likely to be an immune-evasion strategy that contributes to P. aeruginosa-triggered respiratory infections. PMID: 27792459
- IL-22 seems to be the critical cytokine for the development of atopic dermatitis (AD) and is induced in AD model by epicutaneous sensitization with ovalbumin. PMID: 28655472
- finding demonstrated that IL-22 could exert favorable effects on Diabetic nephropathy (DN) via simultaneously alleviating systemic metabolic syndrome and downregulating renal NLRP3/caspase-1/IL-1beta pathway, suggesting that IL-22 might have therapeutic potential for the treatment of DN. PMID: 28726774
- this study shows that IL-22 mediates protective immunity during chronic stages of Mycobacterium tuberculosis HN878 infection in mice PMID: 28247861
- this study shows that hepatocyte responses to IL-22 stimulation are reduced in hypoxic environments PMID: 27796296
- Epithelial IL-23R signaling enables protective IL-22 responses in experimental colitis. PMID: 27524624
- We conclude that IL-22 has an important role in controlling S. aureus nasal colonization through distinct mechanisms, with IL-22 mediating its effect exclusively by inducing AMP expression and controlling availability of staphylococcal ligands. PMID: 27007677
- results reveal that IL-22 increases intestinal epithelial permeability by upregulating Claudin-2 expression through the JAK/STAT pathway PMID: 28939759
- investigated the function of Card9-mediated innate immunity in inflammation-associated colon carcinogenesis; report that Card9-signaling drives the production of IL-1beta within the damaged intestine and regulates the subsequent generation of IL-22 by group3 innate lymphoid cells, which promotes tumorigenesis via STAT3 activation within the transformed epithelium PMID: 28586167
- these results demonstrate that IL-22 has a critical role in vaccine-induced protection against Helicobacter pylori PMID: 27143303
- this study shows for the first time that a defect in IL-22 is involved in the acute exacerbation induced by non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae infection during experimental chronic obstructive pulmonary disease PMID: 27143304
- hypoxic IL-22 upregulation is dependent on HIF-1alpha PMID: 27534553
- Macrophage-derived IL-22 protects hepatocytes from ethanol-induced cell death. IL-22 downregulation is a new regulatory target of LPS in the pathogenesis of AH. PMID: 28637673
- IL-22 inhibits acetaldehyde-induced hepatic stellate cells activation and proliferation, which may be related to nuclear translocation of Nrf2 and increased activity of the antioxidant axis Nrf2-keap1-ARE. PMID: 28373766
- Endogenous IL-22 and hepatic IL-22R signaling play critical roles in controlling pneumococcal lung burden, and systemic IL-22 decreases bacterial burden in the lungs and peripheral organs by potentiating C3 opsonization on bacterial surfaces, through the increase of hepatic C3 expression. PMID: 27456484
- our data suggest that IL-20 subfamily cytokines, particularly IL-20, IL-22, and IL-24, might provide therapeutic benefit for patients with Diabetic foot ulcers (DFU) . PMID: 28125663
- innate immune cell-derived IL-22 is required for efficient liver regeneration and secretion of IL-22 in the regenerating liver is modulated by the ATP receptor, P2X1 PMID: 26853442
- IL-22 and its receptor have a crucial role in the development and pathogenesis of uveitis by facilitating inflammatory cell infiltration. PMID: 27166675
- We therefore postulate IL-22 as an important enhancer of the GC reaction, maintaining chemokine levels for the persistence of GC reactions, essential for the production of autoantibody-secreting plasma cells. Blocking IL-22 might therefore prevent immune-complex deposition and destruction of joints in RA patients. PMID: 27067635
- AhR has a direct role in IL-22 production by Th17 cells in the mouse ear skin, but not by gammadelta T cells, CD4(-) CD8(-) TCRbeta(+) T cells and ILCs. PMID: 27000947
- Taken together, our results demonstrate that Dok-1 and Dok-2 negatively regulate intestinal inflammation, apparently through the induction of IL-17A and IL-22 expression. PMID: 27450811
- Upregulation of IL-22 in combination with a complete loss of its negative regulator IL-22BP, and increased downstream STAT3-signaling in K8(-/-) and K8(-/-)Apc(Min/+) colonic epithelia confirmed that the IL-22 pathway, important in inflammation, proliferation and tissue regeneration PMID: 27234655
- this study shows that serum IL-22/IL-22BP protein ratio strongly correlates with psoriasis severity PMID: 28356382
- data suggest that the influence of IL-22 on autoimmunity is determined in part by the local microenvironment. In particular, IL-22 deficiency exacerbates tissue injury in inflammatory bowel disease, but has no influence on either the hepatocytes or cholangiocytes in the same model. PMID: 27148790
- this study has demonstrated a crucial role for retinoic acid in promoting IL-22 production and tempering dendritic cell function through downregulating S100A4 protein during viral hepatitis PMID: 28363907
- this study shows that losartan and dexamethasone may suppress inflammatory responses in IgA nephropathy by inhibiting IL-22 expression in Th22 cells PMID: 27930971
- Exogenous recombinant IL-22 protects mice against L-arginine-induced severe acute pancreatitis-associated lung injury by enhancing the expression of anti-apoptosis genes through the STAT3 signaling pathway. PMID: 27275094
- Orally administered R848 triggers TLR-7 on CD11c(+) dendritic cells, inducing interleukin-23 (IL-23) expression followed by a burst of IL-22 secretion by innate lymphoid cells, leading to Reg3gamma expression and restoration of colonization resistance against vancomycin-resistant enterococcus. PMID: 26912904
- IL-22 Defect During Streptococcus pneumoniae Infection Triggers Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease PMID: 26870795
- Rag-RORgammat-reporter and Rag KO mice undergoing ischemia reperfusion injury expressed high protein levels of both IL-22 and GFP (RORgammat) PMID: 26341825
- Overexpression of IL-22 significantly reduced the Klebsiella pneumonia infection in the liver and spleen. PMID: 26729763
- IL-22 restrains tapeworm-mediated protection against colitis via regulation of IL-25 expression PMID: 27055194
- IL-22 is involved in plaque formation; IL-22 released by immune cells is involved in activation of vascular repair by stimulating medial SMC dedifferentiation into a synthetic phenotype PMID: 26298743
- cigarette smoke can inhibit the ROCK2-IRF4 axis and modulate T cell production of IL-22 PMID: 26882474
- IL-17A and IL-22 work synergistically to induce antimicrobials and chemokines such as IL-8, components of calprotectin (CP), lipocalin (LCN) and some beta-defensins in both human and primary mouse gastric epithelial cells (GEC) and gastroids PMID: 26867135
- The study demonstrated the probable involvement of gamma delta T cells in the immune response of an organism via the secretion of IL-17 and IL-22. PMID: 26400286
- IL-22 is not required for type 1 diabetes pathogenesis; suggested that IL-22 may have a regenerative and protective role in the pancreatic islets PMID: 26496462
- IL-23, but not IL-17a or IL-22, promotes neutrophil recruitment and inflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression in the colon in response to C. difficile infection. PMID: 26455347
- Data suggest that interleukin 22 (IL-22) plays a pro-inflammatory/pathogenic role in the onset of antigen-induced arthritis (AIA) through apoptosis-associated speck-like Pycard protein (ASC)-dependent stimulation of interleukin-1 beta (IL-1beta) production. PMID: 26330334
- IL-22 can play a previously unappreciated role in controlling leishmania-induced immunopathology PMID: 26285207
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:IL-10 family
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Nectin-4 (NECTIN4), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1 (C5AR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Retinol-binding protein 4 (Rbp4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human V-set and immunoglobulin domain-containing protein 4 (VSIG4), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
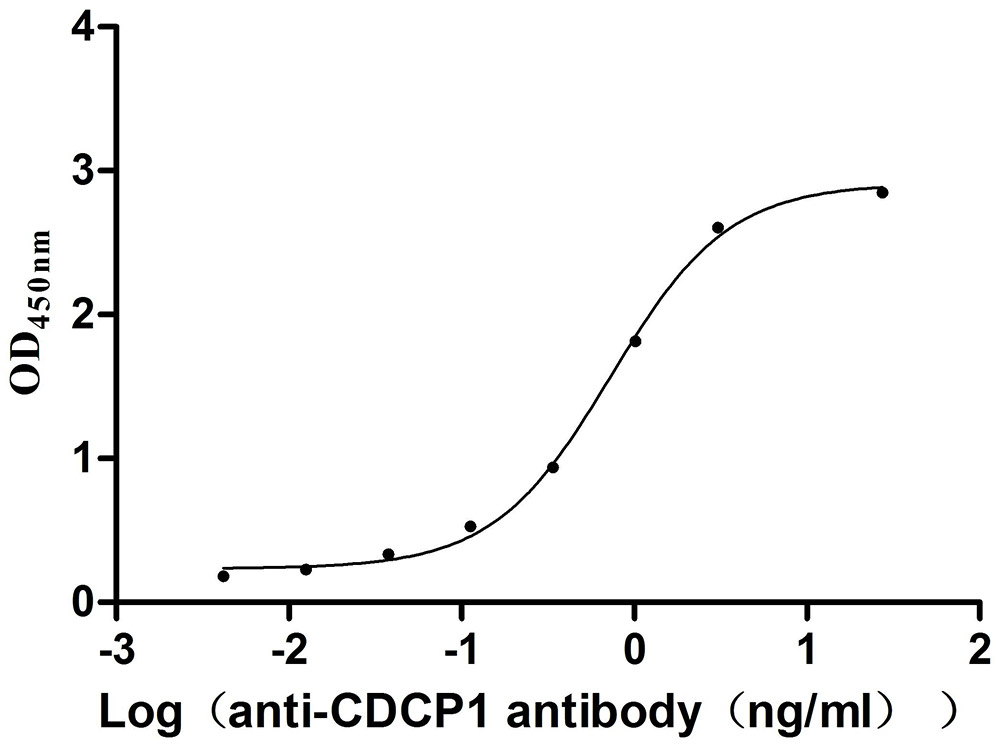
Recombinant Mouse CUB domain-containing protein 1 (Cdcp1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (CRTAM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Cadherin-1(CDH1),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
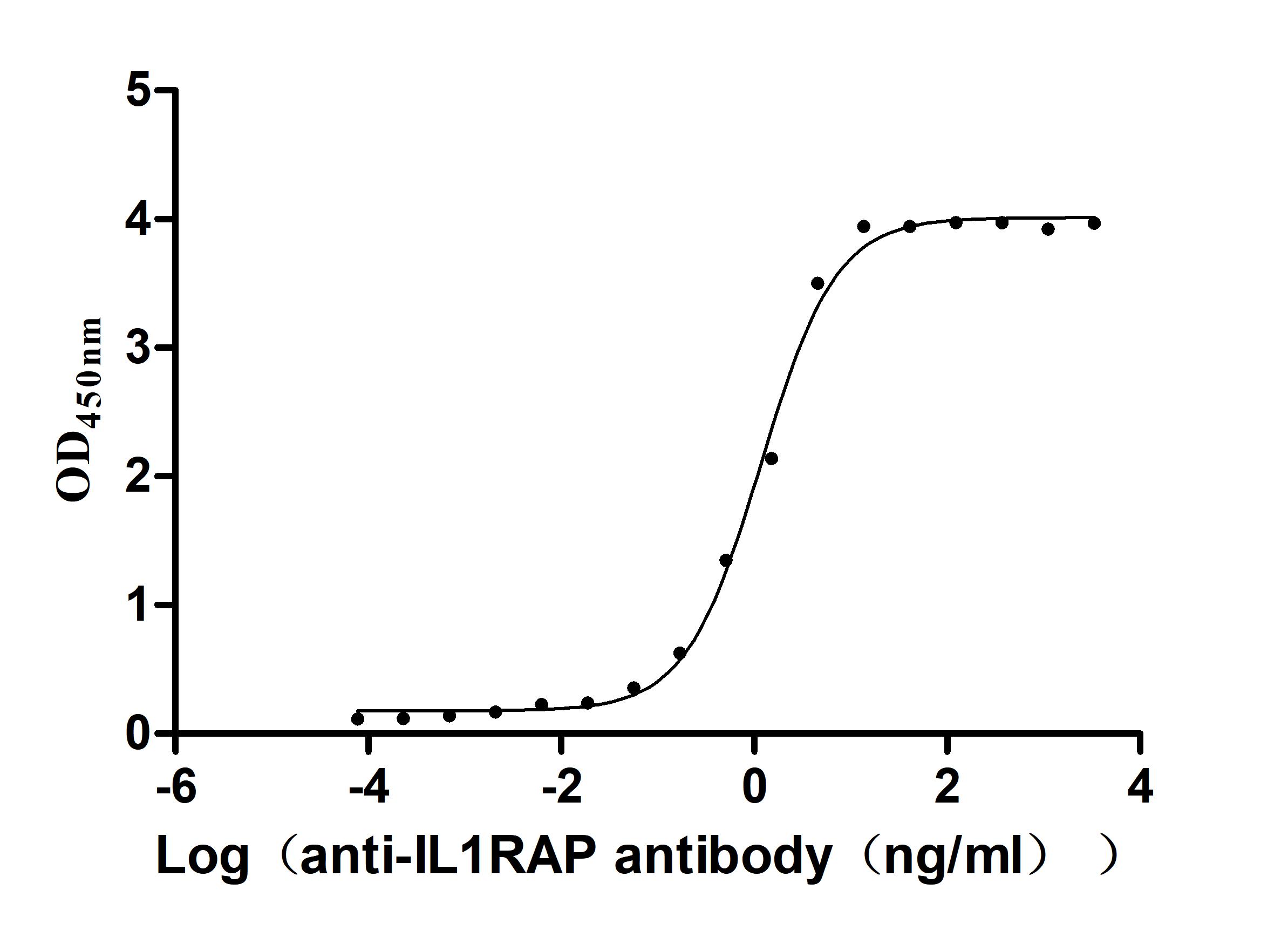
Recombinant Human Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAP), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)